Are you curious about the secrets hidden within your furry friend's heart? Well, get ready to embark on a fascinating journey into the world of feline health as we unravel the mysteries of Saddle Thrombus in cats. This captivating topic holds immense value for both cat owners and animal lovers alike. By understanding this condition, you'll not only be able to provide better care for your beloved pet but also gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of their hearts. So, let's dive right in and decode the enigma of Saddle Thrombus together!
Key Takeaways:
- Saddle thrombus is a life-threatening condition in cats that occurs when a blood clot forms and blocks the main artery supplying blood to the hind limbs.
- Common symptoms of saddle thrombus include sudden paralysis or weakness in the hind legs, cold paws, and pain.
- An echocardiogram is crucial in diagnosing saddle thrombus as it can detect underlying heart conditions that may have contributed to its development.
- Treatment for saddle thrombus typically involves immediate medical intervention to dissolve the blood clot, manage pain, and address any underlying heart issues.
- Prevention of saddle thrombus includes managing underlying heart conditions, ensuring regular veterinary check-ups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle for your cat.
Understanding Saddle Thrombus in Cats: A Guide
What is Saddle Thrombus?
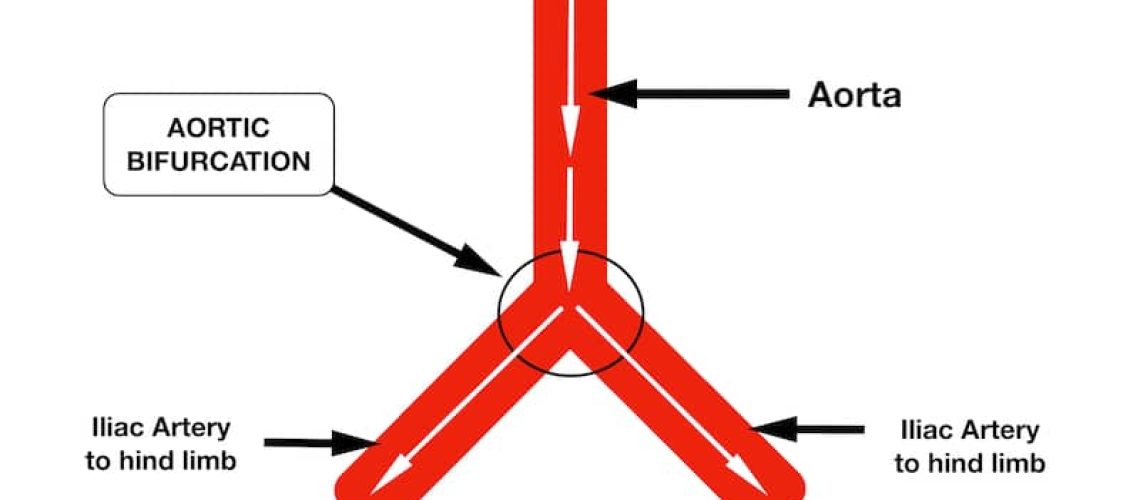
Saddle thrombus, also known as aortic thromboembolism, is a serious condition that affects the hearts of cats. It occurs when a blood clot forms in the heart and then travels through the bloodstream to block an artery. This blockage usually happens at the point where the aorta divides into two branches, resembling a saddle shape, hence the name saddle thrombus. When this occurs, it restricts blood flow to the hind legs.
Why Does Saddle Thrombus Happen?
Saddle thrombus typically occurs in cats with underlying heart disease. The most common cause of this condition is cardiomyopathy, a disease that affects the heart muscle. Cardiomyopathy can weaken the heart and lead to blood clots forming. Other risk factors for saddle thrombus include high blood pressure and certain types of heart valve disease.
- Cardiomyopathy
- High blood pressure
- Heart valve disease
How Does Saddle Thrombus Affect Cats?
When a cat experiences saddle thrombus, it can be extremely painful and distressing for them. The blocked artery prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching their hind legs, causing severe pain and paralysis. The affected leg may feel cold to touch and appear pale or blue due to lack of circulation.
- Severe pain in hind legs
- Paralysis
- Coldness and discoloration in affected leg
The Impact of Saddle Thrombus on Cats' Hearts: What You Need to Know
The Effect on Heart Function
When a blood clot blocks an artery due to saddle thrombus, it disrupts normal blood flow within the heart. This can lead to decreased oxygen supply to the heart muscle, causing damage and potentially leading to heart failure. The heart may struggle to pump blood effectively, resulting in symptoms such as rapid breathing, coughing, and lethargy.
Complications of Saddle Thrombus
Saddle thrombus can have long-term effects on a cat's heart health. It can weaken the heart muscle over time and increase the risk of future blood clot formation. Cats who have experienced saddle thrombus are also at a higher risk of developing congestive heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Decreased oxygen supply to the heart
- Potential for heart failure
- Increased risk of future blood clots
Diagnosing Saddle Thrombus
To diagnose saddle thrombus, veterinarians may perform various tests including physical examination, X-rays, ultrasound, and blood tests. These tests help identify the presence of a blood clot, assess the extent of damage to the hind legs, and determine any underlying causes such as cardiomyopathy or high blood pressure.
- Physical examination
- X-rays and ultrasound
- Blood tests
Recognizing the Symptoms of Saddle Thrombus in Cats: A Quick Guide
Signs and Symptoms
It is important for cat owners to be aware of the signs that may indicate saddle thrombus. Some common symptoms include:
- Sudden hind leg paralysis or weakness
- Coldness and discoloration in one or both hind legs
- Severe pain when touched or movement is attempted
- Rapid breathing or shortness of breath
If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention immediately.
Distinguishing Saddle Thrombus from Other Conditions
The symptoms of saddle thrombus can be similar to other conditions, such as spinal cord injury or nerve damage. However, the sudden onset of hind leg paralysis or weakness, combined with coldness and discoloration in the legs, is a strong indication of saddle thrombus. A veterinarian can perform tests to confirm the diagnosis.
- Hind leg paralysis or weakness
- Coldness and discoloration in legs
- Severe pain when touched or moved
- Rapid breathing
The Importance of Prompt Veterinary Care
Saddle thrombus is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. The longer the blood clot remains untreated, the greater the risk of permanent damage to the affected leg and potential complications for your cat's overall health. Early intervention can help alleviate pain, improve blood flow, and increase the chances of a positive outcome.
- Medical emergency requiring prompt care
- Risk of permanent leg damage if left untreated
- Early intervention improves outcomes
Treating Saddle Thrombus in Cats: Options and Approaches
Emergency Treatment
When a cat is diagnosed with saddle thrombus, immediate treatment is necessary to relieve pain and restore blood flow. Emergency treatment may include:
- Pain medication to alleviate discomfort
- Blood thinners to dissolve or prevent further blood clots
- Medications to improve heart function and circulation
Long-Term Management
After emergency treatment, long-term management focuses on addressing underlying heart disease and reducing the risk of future blood clots. This may involve:
- Medications to manage heart disease (e.g., beta-blockers)
- Dietary changes to support heart health
- Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays an essential role in helping cats recover from saddle thrombus. It includes providing a comfortable environment, assisting with mobility if needed, and ensuring proper nutrition and hydration. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises may also be recommended to improve muscle strength and function.
- Medications for heart disease management
- Dietary changes for heart health
- Supportive care for comfort and recovery
Preventing Saddle Thrombus in Cats: Tips to Keep Your Feline Friend Safe
Managing Underlying Heart Disease
One of the best ways to prevent saddle thrombus in cats is by managing underlying heart disease. Regular veterinary check-ups, appropriate medication, and a heart-healthy diet can help minimize the risk of blood clot formation.
Reducing Stress
Stress can exacerbate heart disease in cats. Creating a calm and stress-free environment, providing enrichment activities, and avoiding sudden changes or disruptions can contribute to overall heart health.
Promoting Exercise
Regular exercise helps maintain good cardiovascular health in cats. Engaging your cat in playtime activities and providing opportunities for physical activity can support a healthy heart.
Spotting a Potential Saddle Thrombus Emergency in Your Cat: What to Look For
Recognizing an Emergency Situation
If you suspect your cat may be experiencing saddle thrombus, it is crucial to act quickly. Look out for these signs that indicate an emergency situation:
- Sudden hind leg paralysis or weakness
- Severe pain or distress
- Coldness or discoloration in the hind legs
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
If any of these symptoms occur, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Avoiding Self-Diagnosis
While it's important to be aware of the symptoms of saddle thrombus, self-diagnosis is not recommended. Only a veterinarian can accurately diagnose this condition through proper examination and diagnostic tests.
Transporting Your Cat Safely
When transporting a cat experiencing a potential saddle thrombus emergency, it's crucial to handle them gently and minimize movement. Use a secure carrier with soft bedding to keep your cat comfortable during the journey to the veterinary clinic.
Possible Long-Term Effects and Complications of Saddle Thrombus in Cats
Long-Term Leg Damage
Saddle thrombus can cause long-term damage to the affected leg. Even with treatment, some cats may experience residual weakness or partial paralysis. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises may be recommended to improve leg strength and mobility.
Risk of Recurrence
Cats who have experienced saddle thrombus are at an increased risk of future blood clot formation. Regular monitoring by a veterinarian and adherence to prescribed medications can help reduce this risk.
Impact on Quality of Life
Saddle thrombus can significantly impact a cat's quality of life. The pain, physical limitations, and potential complications associated with this condition may require ongoing management and care. However, with proper treatment and support, many cats can still enjoy a good quality of life.
- Long-term leg weakness or partial paralysis
- Increased risk of future blood clots
- Potential impact on quality of life
In conclusion, saddle thrombus is a serious condition that affects cats' hearts. It can cause pain, weakness, and difficulty moving. It is important for cat owners to be aware of the signs and seek veterinary help if they suspect their cat may have this condition.
How do you diagnose saddle thrombus in cats?
The diagnosis of saddle thrombus in cats usually involves a combination of clinical signs, thorough physical examination, imaging tests like x-rays and ultrasound, and blood tests. The physical examination may show a lack of pulse or reduced pulse in the hindquarters.
How long will a cat live with a saddle thrombus?
Cats with heart failure and a saddle thrombus have a median survival time of 77 days, while cats with a saddle thrombus but without heart failure have a median survival time of 223 days. Fortunately, permanent limb damage is not common, but it can occur in some cases.
Can you save a cat with saddle thrombus?
A saddle thrombus is a severe condition that unfortunately, even with treatment, most cats do not survive. In order to treat this condition, your cat will need to be hospitalized and receive intensive treatment and nursing care. Your veterinarian will also provide strong pain relief to help manage the intense pain caused by a saddle thrombus.
What percentage of cats survive saddle thrombus?
The outlook for cats with Saddle Thrombus is not very optimistic. Only half of the cats who receive treatment are able to survive and be discharged from the veterinary hospital, and out of that half, only 20% are able to survive for another year. Cats who do not have severe underlying heart disease and regain hind leg function within a few days have the best chances of survival.
What is the diagnostic test for thrombus?
Duplex ultrasonography is a diagnostic imaging test that utilizes sound waves to examine the blood flow in the veins and identify any obstructions or blood clots in the deep veins. This test is considered the standard method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
How long does it take for a thrombus to dissolve?
The time it takes for blood clots to dissolve can vary from weeks to months, depending on their size. If you have a low risk of developing another blood clot, your doctor may prescribe you three months of anticoagulant medication, as advised by the American Heart Association.