Key Takeaways:
- Abscesses in dogs are localized infections that result in the formation of a pocket filled with pus.
- Common causes of abscesses in dogs include bites, wounds, foreign objects, or underlying dental problems.
- Signs of an abscess in dogs may include swelling, pain, redness, discharge, and fever.
- Treatment for abscesses typically involves draining the pus, cleaning the area, and administering antibiotics.
- Preventing abscesses in dogs can be achieved through regular grooming, addressing dental issues promptly, and avoiding situations where they may get into fights or sustain injuries.
Are you a dog lover? Do you want to ensure the health and well-being of your furry friend? Then understanding abscesses in dogs is essential for you! These painful, pus-filled infections can cause discomfort and distress for your canine companion. By delving into this subject, you'll gain valuable knowledge on how to prevent, identify, and treat abscesses, ultimately providing the best care possible for your beloved pet. Did you know that nearly 5% of all dogs will develop an abscess at some point in their lives? With this alarming statistic in mind, it's crucial to equip yourself with the necessary information to protect your four-legged family member. So let's dive into the world of abscesses in dogs and become empowered to keep our furry friends healthy and happy!
What is an abscess in dogs and how does it develop?
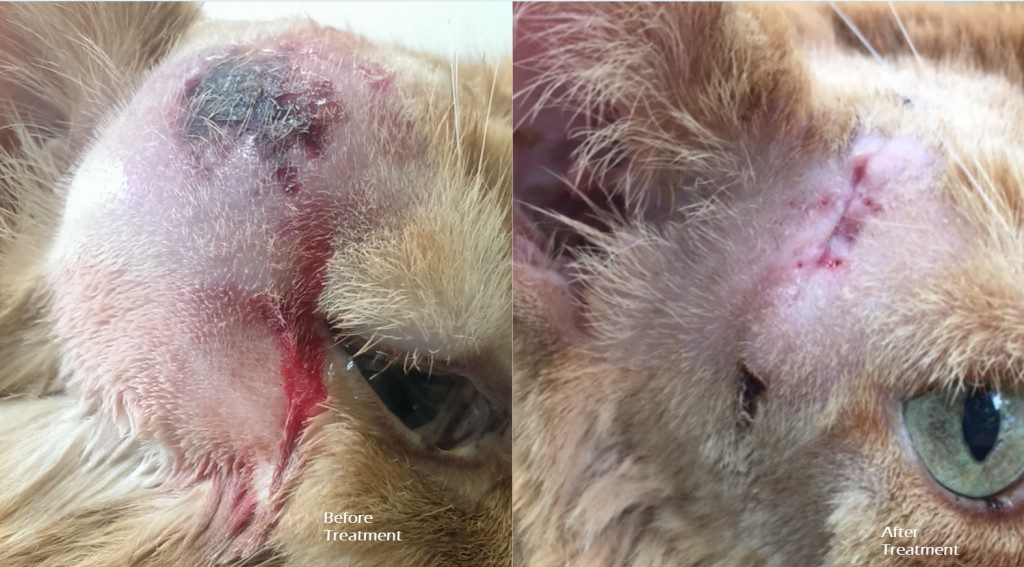
An abscess in dogs is a localized infection that forms a pocket of pus. It usually develops when bacteria enter the body through a wound or injury. The body's immune system responds by sending white blood cells to fight off the infection, leading to the formation of pus. Over time, the pus accumulates and creates pressure, resulting in the formation of an abscess.
The development of an abscess can be influenced by various factors such as poor hygiene, foreign objects getting lodged in the skin, or underlying health conditions that weaken the immune system. Dogs that frequently engage in fights with other animals are also at a higher risk of developing abscesses due to bite wounds.
If left untreated, an abscess can continue to grow and spread infection to surrounding tissues. Therefore, it is important to identify and address abscesses promptly to prevent further complications.
How do bacteria cause an abscess?
When bacteria enter a dog's body through a wound or injury, they can multiply rapidly and trigger an immune response. The immune system sends white blood cells to fight off the infection, which leads to inflammation and the production of pus. The accumulation of pus creates a pocket or cavity within the body known as an abscess.
Common causes of abscesses in dogs
- Bite wounds from fights with other animals
- Scratches or cuts from sharp objects
- Foreign objects embedded in the skin
- Poor hygiene or dirty living conditions
The role of the immune system
The immune system plays a crucial role in fighting off infections and preventing them from spreading throughout the body. When bacteria enter a dog's body through a wound, the immune system recognizes them as foreign invaders and mounts an inflammatory response. This response helps contain the infection by isolating it within the abscess. However, if the immune system is compromised or overwhelmed, it may not be able to effectively control the infection, leading to further complications.
Common signs and symptoms of abscesses in dogs
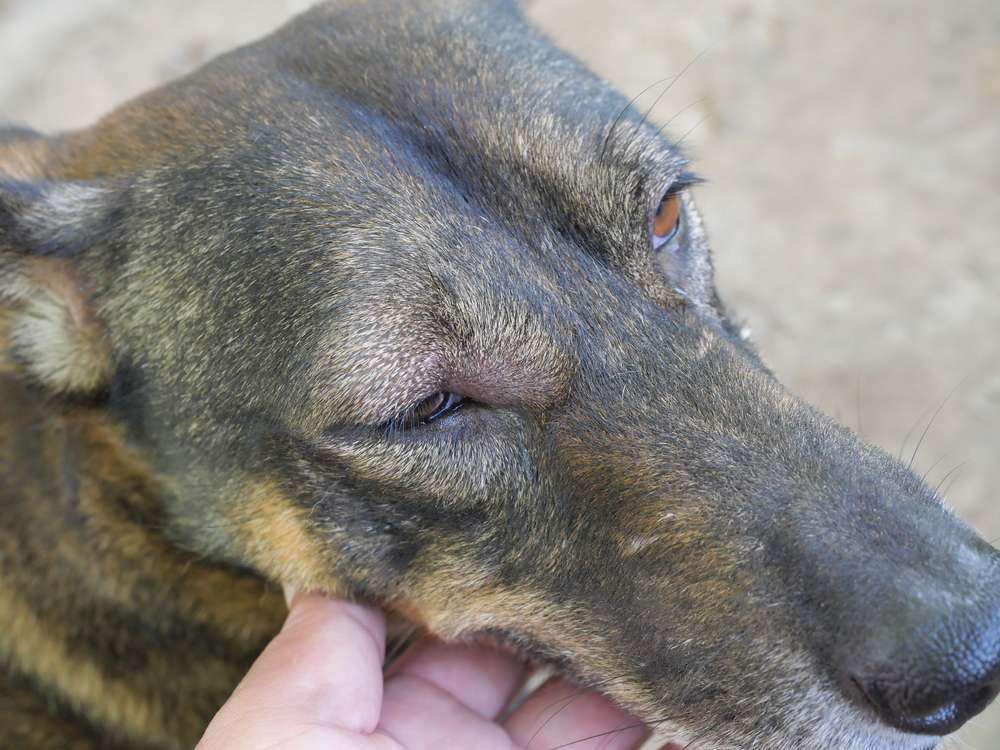
Abscesses are common in dogs and can occur for various reasons, such as bites, puncture wounds, or foreign objects getting stuck under the skin. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of abscesses in dogs to ensure prompt treatment. One common sign is swelling at the affected area, which may feel warm to the touch. The dog may also exhibit pain or discomfort when the area is touched or when they move. In some cases, there may be a visible wound or a pus-filled lump that has formed. Other signs include redness, inflammation, and a foul odor coming from the affected area.
If you notice any of these symptoms on your dog, it is crucial to take action immediately. Abscesses can be painful for your furry friend and may lead to more serious complications if left untreated. By seeking veterinary care promptly, you can ensure that your dog receives appropriate treatment and relief from their discomfort.
Preventing abscesses in your dog
While it's not always possible to prevent abscesses entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk for your beloved pet. One important measure is to keep a close eye on your dog during outdoor activities, especially when they interact with other animals. Dogs are prone to getting into fights or encounters that could result in bite wounds leading to abscesses. By supervising their interactions and intervening if necessary, you can minimize the chances of such injuries occurring.
Another preventive measure is maintaining good hygiene for your dog's skin and coat. Regularly grooming them helps identify any potential issues early on and allows you to address them promptly before they develop into abscesses. Additionally, keeping your dog's living environment clean and free from sharp objects or debris reduces the risk of puncture wounds.
Tips for preventing abscesses in dogs:
- Supervise your dog during outdoor activities and intervene if necessary to prevent fights or bites.
- Regularly groom your dog to identify any skin issues early on.
- Keep your dog's living environment clean and free from sharp objects or debris.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of your dog developing abscesses and ensure their overall well-being.
How to treat a dog's abscess at home
If you notice an abscess on your dog, it is essential to seek veterinary care for proper diagnosis and treatment. However, there are some steps you can take at home to provide temporary relief and prevent further complications before visiting the vet.
Firstly, it is crucial to keep the affected area clean. Gently wash the abscess with warm water and mild antiseptic soap, ensuring that all dirt or debris is removed. Avoid using harsh chemicals or strong disinfectants as they may irritate the wound further. Once cleaned, apply a warm compress to the area for 10-15 minutes several times a day. This helps promote drainage and relieve pain.
It is important not to attempt lancing or draining the abscess yourself as this should be done by a veterinarian under sterile conditions. Instead, focus on keeping the area clean and providing comfort until professional medical assistance can be obtained.
Steps for treating a dog's abscess at home:
1. Gently wash the abscess with warm water and mild antiseptic soap.
2. Apply a warm compress to the area for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
3. Do not attempt lancing or draining the abscess yourself; seek veterinary care for proper treatment.
Remember, these home treatments are only temporary measures and should not replace professional veterinary care. Seeking prompt medical attention will ensure that your dog receives appropriate treatment tailored to their specific condition, preventing any potential complications.
When to seek veterinary care for a dog with an abscess
While some minor abscesses may resolve on their own with proper home care, it is crucial to know when it's time to seek veterinary care for your dog. If the abscess is large, deep, or accompanied by severe pain, it is best to consult a veterinarian immediately. Additionally, if your dog shows signs of systemic illness such as fever, loss of appetite, lethargy, or if the abscess continues to worsen despite home treatment, prompt veterinary attention is necessary.
A veterinarian will assess the abscess and determine the appropriate course of action. This may involve draining the abscess under sterile conditions and prescribing antibiotics to prevent infection. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove any foreign objects or thoroughly clean the affected area.
Remember that early intervention is key in preventing complications and ensuring your dog's well-being. By seeking veterinary care promptly, you can provide your furry friend with the necessary treatment they need for a speedy recovery.
Potential complications and long-term effects of untreated abscesses in dogs
If left untreated, abscesses in dogs can lead to various complications and long-term effects that can significantly impact their health. One common complication is the spread of infection from the initial site to surrounding tissues or even into the bloodstream. This can result in a condition called septicemia or blood poisoning, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
In addition to systemic infections, untreated abscesses can cause chronic pain and discomfort for your dog. The constant presence of an untreated abscess can also weaken their immune system over time, making them more susceptible to other illnesses or infections.
Furthermore, if an abscess remains unresolved for an extended period or becomes recurrent, it may require more invasive treatments such as surgery or long-term antibiotic therapy. These treatments can be costly and may involve additional risks for your dog.
To avoid these potential complications and long-term effects, it is crucial to seek veterinary care as soon as you notice any signs of an abscess in your dog. By doing so, you can ensure that appropriate treatment is provided promptly, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting a full recovery for your furry companion.
Potential complications and long-term effects of untreated abscesses in dogs
1. Infection spread
If left untreated, abscesses in dogs can lead to the spread of infection throughout their bodies. The pus-filled pockets can burst and release harmful bacteria into the bloodstream, causing a condition called septicemia. This can result in severe illness and even death if not promptly addressed by a veterinarian.
Signs of infection spread:
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Rapid breathing or panting
- Increased heart rate
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, as they could indicate a spreading infection from an untreated abscess.
2. Damage to surrounding tissues
Abscesses that are left untreated can cause damage to the surrounding tissues. As the infection progresses, it can destroy healthy cells and tissue structures, leading to further complications. In some cases, this damage may be irreversible and require surgical intervention for repair.
Long-term effects:
- Scarring: Untreated abscesses can leave behind unsightly scars on your dog's skin.
- Tissue necrosis: The destruction of tissues due to prolonged infection may result in areas of dead tissue known as necrosis.
- Chronic pain: Dogs with untreated abscesses may experience ongoing pain and discomfort due to the damage caused by the infection.
It is essential to address abscesses promptly to minimize the risk of long-term complications and ensure your dog's overall well-being.
Remember, I'm here to provide information on potential complications and long-term effects of untreated abscesses in dogs. If you have any concerns about your furry friend's health, always consult with a qualified veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
In conclusion, abscesses in dogs are painful infections that can occur under the skin or in different parts of their body. It is important to seek veterinary care promptly if you suspect your dog has an abscess, as treatment is necessary to prevent further complications and promote healing.
How do you treat an abscess on a dog?
If the abscess has not naturally ruptured, your vet will conduct a small surgical procedure to release the pus. Antibiotics will be prescribed to treat the infection and prevent it from spreading in your pet's body, regardless of whether the abscess burst or was drained by the vet.
How serious is an abscess in a dog?
It is important to remember that if your pet is showing any other signs, such as fever, lack of appetite, or low energy, it is imperative that you seek immediate veterinary assistance. If an abscess is left untreated, it can spread the infection to other parts of the body and potentially lead to the death of your dog.
How do you treat an abscess on a dog at home?
To treat the abscess, dampen a cloth with warm water and gently place it on the affected area for 5-10 minutes, repeating this process 4-5 times a day. This will improve circulation, aid in healing, and remove harmful substances. It will also ensure the wound remains open for drainage.
What causes abscess in dogs?
One of the main reasons dogs develop abscesses is due to bite wounds caused by other animals, which introduce infectious organisms deep into the dog's tissue. This is particularly prevalent in dogs that frequently engage in fights with other dogs or have encounters with cats that result in scratches or bites. However, any animal bite has the potential to become infected and develop an abscess.
Can a dog's abscess heal on its own?
Can a dog abscess heal without treatment? Small skin abscesses may rupture, drain, and heal without intervention. Nonetheless, it is advisable to have a veterinarian examine the abscess for any underlying issues that may require attention.
Can I put Neosporin on my dogs abscess?
While Neosporin is typically considered safe for dogs, excessive ingestion can potentially make them ill. Alternatively, you can utilize wound care ointments and medicated wipes specifically designed for pets to prevent infection. If your dog's wound continues to bleed and requires a bandage, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian.