Are you a cat lover who wants to ensure your furry friend is breathing easy? Then, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of bronchitis in cats. This topic is not only essential for understanding the health of your feline companion, but it also holds the key to unlocking a happier, healthier life for them. With clear and simple language suitable for a 7th grader, we'll explore everything you need to know about this common respiratory condition. From its causes and symptoms to effective treatments and preventive measures, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to keep your cat's lungs purring like a well-oiled machine. So, let's embark on this journey together and help your beloved pet breathe easy again!
Key Takeaways:
- Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition in cats that causes inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
- Common symptoms of bronchitis in cats include coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
- Treatment for bronchitis in cats often involves medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Avoiding environmental triggers, such as cigarette smoke or dusty environments, can help prevent and manage bronchitis in cats.
- Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring can help ensure early detection and proper management of bronchitis in cats.
What is Bronchitis in Cats and How Does it Affect Their Breathing?
Bronchitis in cats is a condition where the airways in their lungs become inflamed. This inflammation can make it difficult for cats to breathe properly. The airways, also known as bronchi, become swollen and produce excess mucus, which can block the flow of air. When this happens, cats may experience coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
When a cat has bronchitis, their breathing may become more labored and they may have to work harder to get enough oxygen. They may also develop a persistent cough that can be dry or produce phlegm. Cats with bronchitis may also experience fatigue and loss of appetite due to the strain on their respiratory system.
How Does Bronchitis Affect Cat's Breathing?
Bronchitis affects a cat's breathing by causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways in their lungs. This makes it harder for air to flow freely into and out of the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties. The excess mucus produced during bronchitis further obstructs the airways, making it even more challenging for cats to breathe normally.
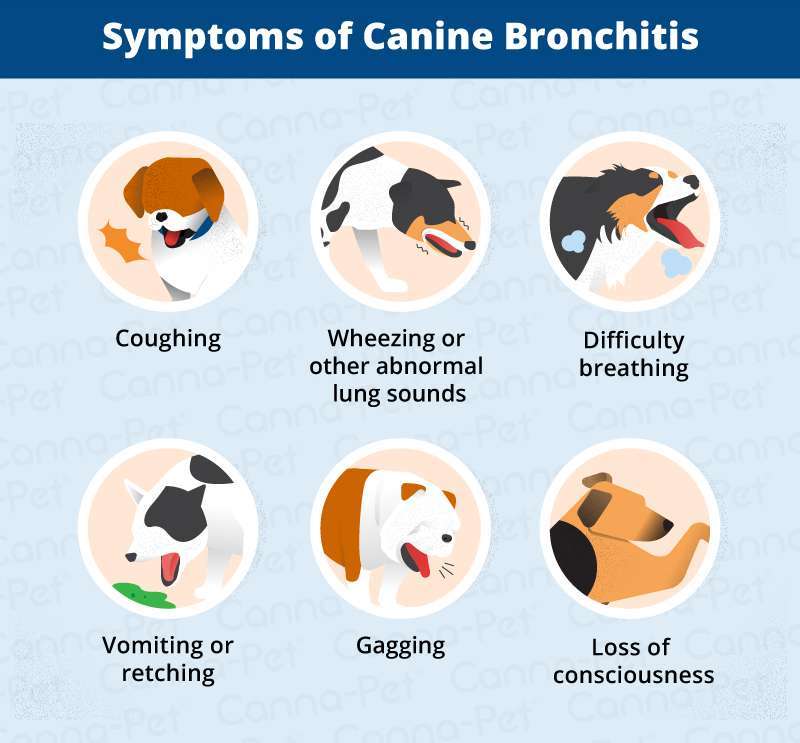
Common Symptoms of Bronchitis in Cats:
- Coughing (dry or with phlegm)
- Wheezing or noisy breathing
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Fatigue or lethargy
- Loss of appetite
It's important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity depending on the individual cat and the stage of bronchitis they are experiencing. If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, it's essential to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Identifying Bronchitis in Cats: Common Symptoms to Look Out For
Identifying bronchitis in cats can be challenging as the symptoms can be similar to other respiratory conditions. However, there are common signs to look out for that may indicate bronchitis in your cat.
Coughing is one of the most noticeable symptoms of bronchitis in cats. They may have a persistent cough that can be dry or produce phlegm. Wheezing or noisy breathing is another sign to watch for. If you hear your cat making unusual sounds while breathing, it could be a result of inflamed airways.
Additionally, cats with bronchitis may exhibit difficulty breathing or shortness of breath. You may notice them breathing more rapidly or using their abdominal muscles to help them breathe. Fatigue and lethargy are also common symptoms, as the effort required to breathe with inflamed airways can leave cats feeling tired.
Diagnosing Bronchitis in Cats: Tests and Examinations
To diagnose bronchitis in cats, a veterinarian will perform a thorough examination and may recommend additional tests. During the examination, they will listen to your cat's lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds such as wheezing or crackling.
In some cases, the vet may suggest chest X-rays to get a better view of the lungs and rule out other potential causes of respiratory issues. They may also perform blood tests to assess overall health and check for any underlying conditions that could contribute to bronchitis.
In certain situations where the diagnosis is still uncertain, the vet may recommend a procedure called bronchoscopy. This involves inserting a small camera into the airways of the cat under anesthesia to visualize any inflammation or abnormalities directly.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment options can be discussed with the veterinarian.
Diagnosing Bronchitis in Cats: Tests and Examinations
Bronchitis in cats can be challenging to diagnose as the symptoms may overlap with other respiratory conditions. To determine if a cat has bronchitis, veterinarians will conduct a series of tests and examinations.
Firstly, a thorough physical examination will be performed. The veterinarian will listen to the cat's lungs using a stethoscope to check for abnormal breathing sounds such as wheezing or crackling. They may also observe the cat's breathing rate and effort.
Next, diagnostic imaging techniques like X-rays or ultrasound may be used to visualize the cat's lungs and airways. This can help identify any abnormalities or inflammation present.
In some cases, a bronchoscopy may be necessary. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the cat's airways to directly visualize the bronchi and collect samples for further analysis.
Additional tests such as blood work, including complete blood count (CBC) and biochemistry profile, may be conducted to assess overall health and rule out other underlying conditions.
Overall, diagnosing bronchitis in cats requires a combination of physical examinations, diagnostic imaging, and sometimes more invasive procedures like bronchoscopy to accurately identify the condition.
Treating Bronchitis in Cats: Available Options and Recovery Time
Treating bronchitis in cats aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and improve respiratory function. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the condition and individual cat's needs.
One common approach is medication therapy. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids are often prescribed to reduce airway inflammation and relieve coughing. These medications can be administered orally or through inhalation using devices like metered-dose inhalers specifically designed for cats.
In addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, bronchodilators may also be prescribed. These medications help relax the muscles surrounding the airways, allowing for easier breathing. Bronchodilators can be given orally or through inhalation as well.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is suspected or present. However, it's important to note that bronchitis in cats is often caused by viral or non-infectious factors, so antibiotics are not always necessary.
Recovery time for cats with bronchitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual response to treatment. Some cats may show improvement within a few weeks, while others may require long-term management. Regular follow-up visits with the veterinarian are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Preventing Bronchitis in Cats: Steps Cat Owners Can Take
As a cat owner, there are steps you can take to help prevent bronchitis in your feline companion. By implementing these measures, you can promote good respiratory health and reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Firstly, maintaining a clean and dust-free environment is crucial. Regularly vacuuming and dusting your home helps minimize airborne irritants that could trigger respiratory issues. Avoid using strong cleaning products or aerosols that may irritate your cat's airways.
Secondly, ensure proper ventilation in your home. Fresh air circulation helps remove pollutants and keeps the air quality optimal for your cat's respiratory system. Opening windows or using fans can assist in achieving this.
Thirdly, avoid exposing your cat to secondhand smoke. Smoking is harmful not only for humans but also for pets. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke can significantly damage a cat's lungs and increase the risk of developing bronchitis.
Lastly, maintaining overall good health through regular veterinary check-ups and vaccinations is essential. Keeping up with preventive care ensures any underlying conditions are promptly addressed before they lead to respiratory problems.
By following these preventive measures, you can help safeguard your cat's respiratory health and minimize the chances of bronchitis occurring.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Effects of Bronchitis in Cats
Bronchitis in cats, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to various complications and long-term effects. It is crucial to understand these potential consequences to ensure proper care for your feline companion.
One possible complication is the development of secondary bacterial infections. The inflamed airways provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to respiratory tract infections. These infections can worsen symptoms and prolong recovery time.
Chronic bronchitis is another long-term effect that may occur. In some cases, despite treatment, the inflammation in the airways becomes persistent and irreversible. This can result in ongoing coughing, difficulty breathing, and reduced quality of life for the affected cat.
Additionally, bronchitis can increase the risk of developing other respiratory conditions such as asthma or pneumonia. The compromised airways make cats more susceptible to these diseases, which can further complicate their respiratory health.
Furthermore, prolonged inflammation in the lungs can lead to scarring and fibrosis. This thickening of lung tissue restricts airflow even more, making it increasingly difficult for cats to breathe properly.
To prevent these complications and long-term effects, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial. Regular veterinary check-ups and diligent management of bronchitis symptoms are essential to minimize the impact on your cat's respiratory health.
Managing Bronchitis in Cats: Tips for Helping Them Breathe Easy Again
If your cat has been diagnosed with bronchitis, there are several tips you can follow to help them breathe easier and manage their condition effectively.
Firstly, create a calm and stress-free environment for your cat. Stress can exacerbate respiratory symptoms, so providing a peaceful atmosphere helps reduce anxiety levels. Ensure they have a quiet and comfortable space to rest.
Secondly, consider using a humidifier in your home. Moist air can help soothe the inflamed airways and alleviate coughing. However, it's important to clean and maintain the humidifier properly to prevent the growth of mold or bacteria that could worsen respiratory issues.
Thirdly, monitor your cat's weight. Obesity can put additional strain on their respiratory system, making breathing more difficult. Consult with your veterinarian about appropriate diet and exercise plans to help your cat maintain a healthy weight.
Additionally, avoid exposure to environmental irritants such as cigarette smoke, strong odors, or dusty environments. These can trigger or worsen bronchitis symptoms. Keep your home well-ventilated and free from potential respiratory irritants.
Lastly, follow the prescribed medication regimen strictly. Administer medications as directed by your veterinarian and ensure you understand proper dosage and administration techniques. Regularly communicate with your veterinarian about any changes in symptoms or concerns.
By implementing these management tips, you can provide support for your cat's respiratory health and improve their overall well-being while living with bronchitis.
In conclusion, bronchitis in cats can make it difficult for them to breathe, but with proper treatment and care, they can start breathing easy again. It's important to consult a veterinarian if your cat shows signs of bronchitis to ensure their well-being.
How long does it take for a cat to recover from bronchitis?
Bronchitis can be either short-term and reversible, known as acute bronchitis, or lasting for 2 or more months, known as chronic bronchitis. In cats, chronic bronchitis is sometimes mistakenly referred to as feline asthma, even though it is not actually a form of asthma.
How long does difficulty breathing last with bronchitis?
Bronchitis typically resolves within two weeks for the majority of individuals, although recovery may extend up to three to six weeks. During this time, you can ease your symptoms by using over-the-counter medications at home. However, if your condition does not improve after three weeks, it is advisable to seek medical attention from a healthcare provider.
Can bronchitis get worse after getting better?
If you have chronic bronchitis, your symptoms will worsen if you continue to be exposed to the irritants that initially caused the bronchitis or if you also have COPD.
How long can a cat live with bronchitis?
Cats suffering from chronic bronchitis can live a normal life with proper management and experience a high quality of life. However, there may be occasional relapses during seasonal changes or when the air quality is low. In such cases, adjustments to medication dosages may be required. It is recommended to seek advice from your veterinary clinic for personalized guidance.
What are the recovery symptoms of bronchitis?
Typically, individuals with acute bronchitis should start feeling better within one to two weeks, although they may experience a persistent cough and fatigue for three weeks or longer. The viruses and bacteria responsible for bronchitis usually enter your system two to six days before you begin experiencing symptoms similar to a common cold.
How can I help my cat with bronchitis?
If a bacterial infection is detected, cats with bronchitis can receive broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. Using mist or steam from a hot shower can help to loosen secretions and make them easier to cough up. It is also important for cats to have warmth, rest, and maintain proper hygiene.