Key Takeaways:
- Elbow dysplasia is a common orthopedic condition in dogs, particularly large and giant breeds.
- It is caused by abnormal development of the elbow joint, leading to pain, lameness, and decreased mobility.
- Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing elbow dysplasia and preventing further joint damage.
- Treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, weight management, and sometimes surgery.
- Breeding dogs with good elbow health and avoiding excessive exercise during growth stages can help reduce the risk of elbow dysplasia in future generations.
Are you a dog lover? Do you want to ensure the health and well-being of your furry friend? Then, understanding the topic of elbow dysplasia in dogs is essential for you. Elbow dysplasia is a common condition that affects many dog breeds, causing pain and discomfort in their joints. By delving into this subject, you will gain valuable insights into how to prevent and manage this condition, ensuring a happy and active life for your canine companion. Did you know that up to 25% of all dogs suffer from elbow dysplasia at some point in their lives? Don't worry, though – there are effective ways to mitigate the impact of this condition! So, let's dive into the world of elbow dysplasia in dogs and discover how we can keep our furry friends healthy and thriving.
Understanding Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
What is Elbow Dysplasia?
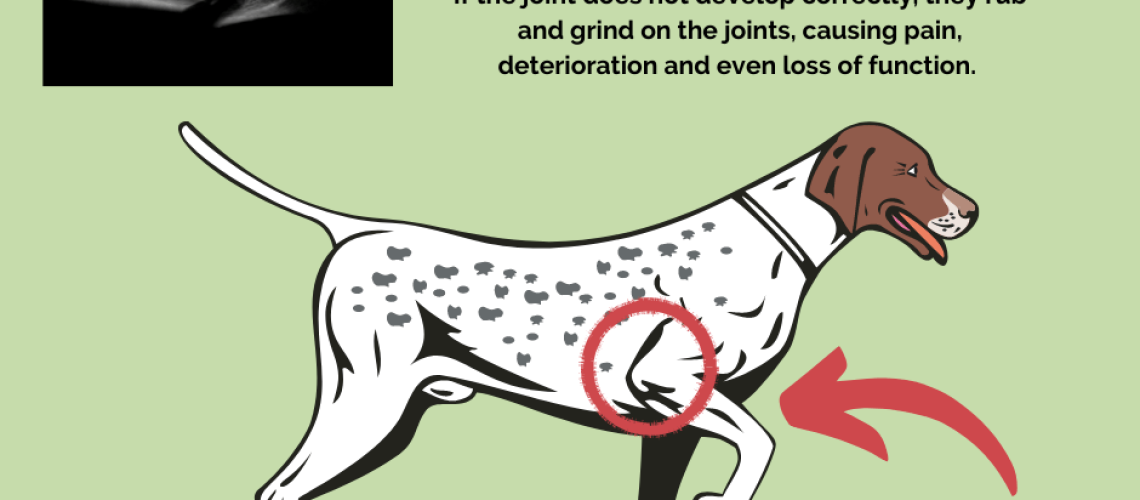
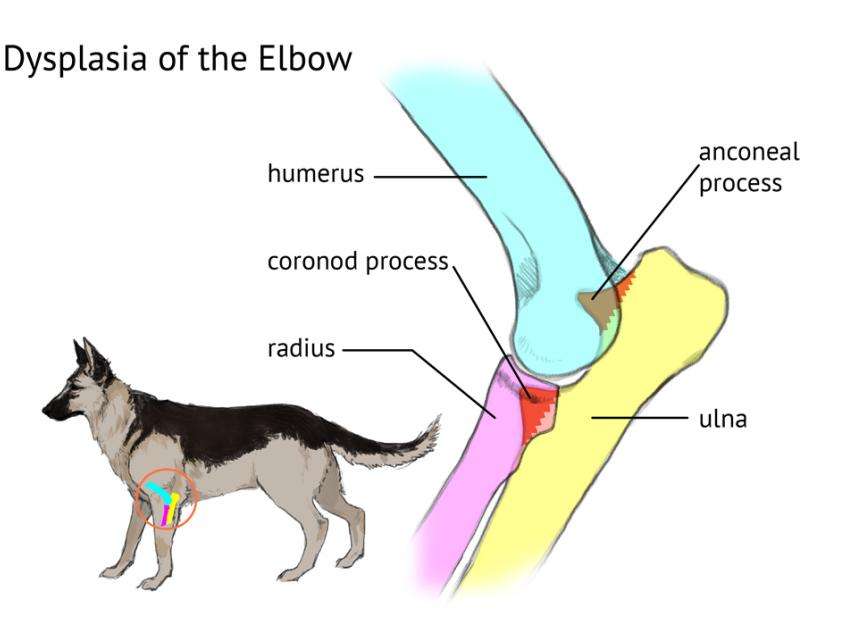
Elbow dysplasia is a common orthopedic condition that affects dogs, particularly larger breeds. It occurs when the bones and joints in the elbow don't develop properly, leading to abnormal growth and movement. This can cause pain, lameness, and difficulty in performing regular activities. Elbow dysplasia is considered a genetic disorder, meaning it can be passed down from one generation to another.
Causes of Elbow Dysplasia
The exact cause of elbow dysplasia is not fully understood, but genetics and rapid growth play significant roles. Certain dog breeds are more prone to developing this condition due to their genetic makeup. Additionally, puppies that grow too quickly or have poor nutrition are at higher risk for developing elbow dysplasia. The excessive stress placed on the developing bones and joints during rapid growth can lead to abnormalities.
The Role of Genetics and Rapid Growth in Elbow Dysplasia
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in the development of elbow dysplasia. Certain dog breeds have a higher prevalence of this condition due to specific genes that contribute to abnormal joint formation. Breeding two dogs with a history of elbow dysplasia increases the likelihood of their offspring inheriting the condition. Responsible breeders take measures to reduce the incidence of elbow dysplasia by screening breeding dogs for this condition.
Rapid Growth and Nutrition
Rapid growth during puppyhood can also contribute to the development of elbow dysplasia. Puppies that gain weight too quickly or receive an unbalanced diet may put excessive stress on their growing bones and joints. Proper nutrition and controlled growth are essential for healthy bone development in puppies. It's important to provide a balanced diet and avoid overfeeding to prevent the onset of elbow dysplasia.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
Lameness and Stiffness
One of the most common signs of elbow dysplasia in dogs is lameness or limping, especially after exercise or prolonged rest. Affected dogs may also exhibit stiffness in their front legs. They may have difficulty getting up from lying down or show reluctance to engage in physical activities that require the use of their front legs.
Pain and Discomfort
Dogs with elbow dysplasia often experience pain and discomfort in their affected joints. They may show signs of sensitivity when their elbows are touched or manipulated. They might also exhibit a decreased range of motion in the affected leg, leading to difficulty performing regular movements like climbing stairs or jumping.
Joint Swelling and Crepitus
In some cases, dogs with elbow dysplasia may develop joint swelling due to inflammation. The affected joint may appear swollen, warm to the touch, or even feel fluid-filled. Additionally, crepitus, which is a crackling sound or sensation when moving the joint, can be observed.
Preventing Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs: Essential Measures to Take
Selecting a Responsible Breeder
When getting a dog from a breeder, it's crucial to choose a responsible breeder who prioritizes the health and well-being of their breeding dogs. A reputable breeder will conduct health screenings on their breeding dogs for conditions like elbow dysplasia. They will also provide information about the genetic history of their dogs to ensure you're getting a puppy with lower risk for developing this condition.
Maintaining Healthy Growth
Proper nutrition and controlled growth are essential in preventing elbow dysplasia. Feeding a balanced diet and avoiding overfeeding can help ensure that puppies grow at a healthy rate. It's important not to rush the growth process, as rapid growth can put excessive stress on developing joints. Regular exercise should also be provided, but it should be low-impact and appropriate for the puppy's age and breed.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for early detection and prevention of elbow dysplasia. Your veterinarian can perform physical examinations, assess your dog's gait, and evaluate their joint health. They may also recommend X-rays or other diagnostic tests to determine if there are any abnormalities in the elbows. Early intervention and management can significantly improve the long-term prognosis for dogs with elbow dysplasia.
Dog Breeds Prone to Elbow Dysplasia: What You Need to Know
Large and Giant Breeds
Elbow dysplasia is more commonly seen in larger dog breeds, especially those classified as giant breeds. Breeds such as Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherds, Rottweilers, Bernese Mountain Dogs, and Great Danes have a higher prevalence of this condition compared to smaller breeds.
Hereditary Predisposition
Certain dog breeds have a higher genetic predisposition to elbow dysplasia due to specific genes that contribute to abnormal joint development. Breeders of these susceptible breeds should prioritize health screenings on their breeding dogs to reduce the incidence of this condition in future generations.
Diagnosing and Treating Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs: Veterinary Insights
Veterinary Examination
To diagnose elbow dysplasia, veterinarians will conduct a thorough physical examination of the affected dog. They will assess their gait, range of motion, and perform joint manipulation to evaluate any pain or abnormalities. X-rays or other imaging techniques may be used to visualize the elbow joints and identify any structural abnormalities.
Treatment Options
The treatment for elbow dysplasia depends on the severity of the condition and the individual dog. Mild cases may be managed through conservative measures such as weight management, controlled exercise, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. In more severe cases, surgical interventions like arthroscopy, joint replacement, or corrective osteotomy may be necessary to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Long-term Management
Elbow dysplasia is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management. Regular veterinary check-ups are important to monitor the progression of the disease and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Weight management is crucial to reduce stress on the affected joints. Additionally, providing appropriate exercise and physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and joint mobility. With proper care and management, dogs with elbow dysplasia can lead happy and comfortable lives.
In conclusion, elbow dysplasia is a common joint problem in dogs that can cause pain and discomfort. It is important for dog owners to be aware of this condition and take steps to prevent and manage it to ensure their furry friends live healthy and happy lives.
How long will my dog live with elbow dysplasia?
The lifespan of a dog with elbow dysplasia is not significantly affected by the condition. However, reduced activity levels due to discomfort may lead to problems like obesity. By maintaining a healthy diet, providing regular exercise, and giving proper treatment, you can ensure that your dog remains healthy and enjoys a good quality of life.
What are the first signs of elbow dysplasia in dogs?
Dogs that are typically affected exhibit signs of lameness in one or both of their front legs, stiffness (particularly after resting), and a lack of desire to engage in physical activity. It is common for the front feet to appear turned outward. Descending stairs can be uncomfortable due to soreness in the elbows.
Can you fix elbow dysplasia in dogs?
Although elbow dysplasia cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed. Through surgical intervention and appropriate medical treatment, many dogs can have a positive long-term outlook.
What are 4 causes of elbow dysplasia in dogs?
The main cause of elbow dysplasia in dogs is believed to be genetic and related to their development. Other potential factors that may contribute to this condition include rapid growth, a high protein diet, trauma, hormonal imbalances, inadequate nutrition, sudden weight gain, and the amount of exercise they receive.
How much does it cost to fix a dog's elbow dysplasia?
Treating elbow dysplasia can be expensive. Whether your dog is in the early stages of pain or has advanced arthritis, the expenses can accumulate. For younger dogs who are eligible for surgical solutions, the cost of diagnosis and treatment can range from $1,500 to $4,000 per elbow.
Can a dog live with elbow dysplasia without surgery?
Elbow dysplasia is a condition that causes pain and requires lifelong treatment. While some dogs can find relief through daily management techniques such as controlling their weight, exercise, and pain relief, others may not respond as well and may require surgery. With proper treatment, dogs can live a long and happy life.