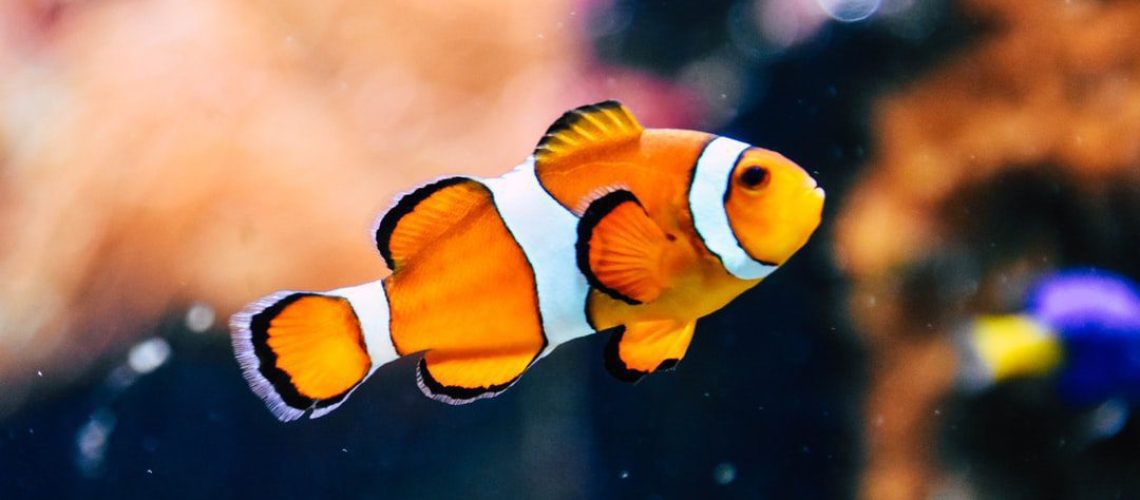
Freshwater fishes come in various shapes and sizes, including those with elongated bodies and those with pear-shaped bodies. They generally have no appendages and feed by sucking plant or animal matter. Although most freshwater fishes live in fresh water, saltwater fishes also exist.
All live in rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams. Freshwater fishes include many perch fishes and catfish.
- Fishes are bony, flesh-and-scales animals.
- They are separated into two sister groups, including the echinoderms and the tunicates.
- These groups further divide into classes such as bony prominences, which include such fishes as the channel catfish, the flathead catfish, the rainbow fish, the barracuda, the Sailfish, the stonefish, the bull shark, the bluefish, and the surgeonfish.
The echinoderms have paired organs called gills; these organs are situated near the mouth, on the sides of the head, inside the jaws, in the throat, and on the fins. The other class of echinoderms is composed of cephalopods and tube fishes.
Fishes are part of the animal kingdom Trichophyton: Fishes are an important part of ecosystem as they filter the water, eliminate waste products, adjust oxygen levels, and consume food. Fish farming is one of the industry activities now leading to depletion of fishes in the wild. The fish farming industry helps in protecting fish stocks by raising fish under controlled conditions.
Fishes have evolved over time: as the basis of an intricate physical makeup. Fish anatomy includes five pairs of paired fins, with each pair having a unique position, function, and use. The fifth pair of fins is called gill covers or gills. A fish's eyes are located on the top of its head and protrude slightly beyond the gill covers. The remainder of the fish body including the tail, dorsal fin, caudal fin, pelvic fin, pectorals, limbs, head, horns, teeth, toes, and horns are covered with scales.
Fishes belong to a class called Prototheria: Among other bony fishes, sharks, anemones, bivalves, molluscs, and cephalopods are regarded as prototherians. The word "prototheria" derives from the Greek word meaning "other". It refers to a number of cephalopods and bivalves including the anemone, butterfly fish, damselfly, ghost shrimp, and box jellyfish. The term "cartilaginous sharks" refers to the sole functioning of cartilage in sharks and cuttlefish and their close relatives.
In addition to sharks and cephalopods: there are two main sister groups of fishes. These groups are Prototheria and Metatheria. Within the Metatheria group there are two general types of fishes: land and freshwater. Both the land and freshwater belong to the Prototheria group while the anemone is a member of the Metatheria group. Within the Metatheria group there are three basic types of fishes.
The common bullfish, the common rainbow trout, and the gray-colored black-finned flycatcher.