Key Takeaways:
- Folliculitis in dogs is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of hair follicles.
- It can be caused by various factors such as bacterial or fungal infections, allergies, hormonal imbalances, or parasites.
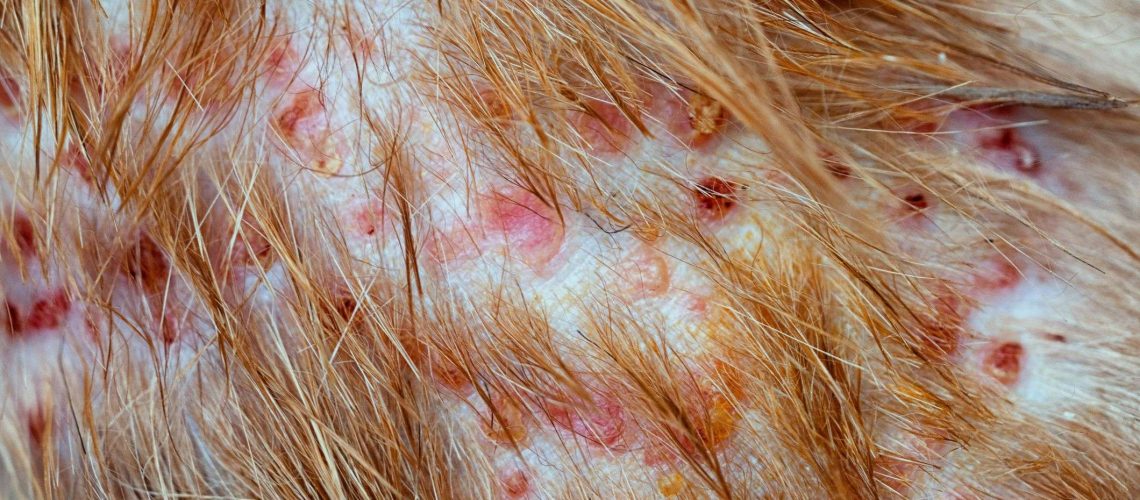
- Symptoms of folliculitis in dogs include redness, swelling, itching, and the formation of pustules or crusts on the skin.
- Treatment typically involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause, which may require medication, topical treatments, or changes in diet or environment.
- Preventing folliculitis in dogs involves regular grooming, maintaining proper hygiene, avoiding potential irritants or allergens, and ensuring a balanced diet for optimal skin health.
Are you a dog lover? If so, then understanding the ins and outs of folliculitis in dogs is essential for your furry friend's well-being. Imagine being able to spot the signs and symptoms early on, ensuring prompt treatment and relief for your loyal companion. By delving into this topic, you'll gain valuable insights into how to prevent and manage this common skin condition in dogs. Did you know that approximately 14% of all canine dermatological cases are attributed to folliculitis? With this knowledge, you'll be equipped to provide the best care possible for your four-legged friend. So let's dive into the world of folliculitis in dogs and become a proactive pet parent!
Understanding Folliculitis in Dogs and Its Effects on Their Skin
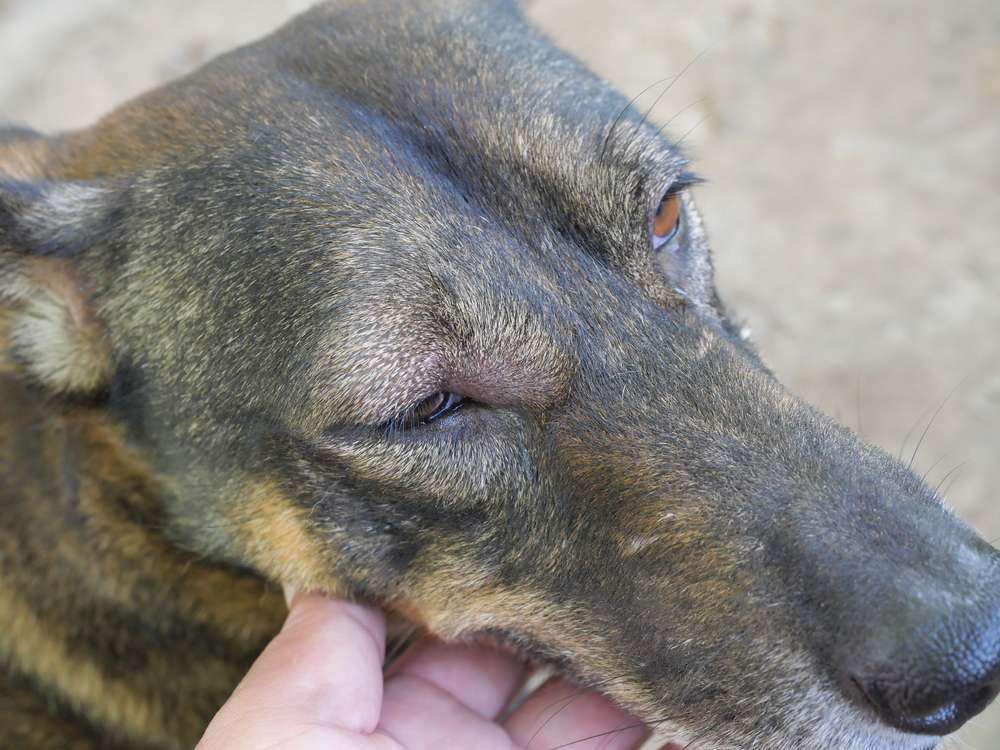
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that can affect dogs. It occurs when the hair follicles in their skin become inflamed or infected. This can happen due to various reasons, such as bacteria, fungus, parasites, or even allergies. When dogs have folliculitis, it can cause redness, itching, and small bumps or pustules on their skin.
The effects of folliculitis on a dog's skin can be uncomfortable and irritating. The constant itching and scratching can lead to further inflammation and even secondary infections. In severe cases, the affected areas may become painful and develop crusts or scabs. If left untreated, folliculitis can spread to other parts of the body and cause more serious complications.
Signs of Folliculitis in Dogs:
- Redness or inflammation of the skin
- Itching or scratching
- Bumps or pustules on the skin
- Hair loss in affected areas
- Pain or discomfort
How Dogs Can Develop Folliculitis and the Signs to Watch Out For
Dogs can develop folliculitis for several reasons. One common cause is poor hygiene or grooming practices. When dogs are not regularly bathed or groomed, dirt and bacteria can accumulate on their skin, leading to infection. Other factors that can contribute to folliculitis include allergies to certain substances like pollen or certain ingredients in grooming products.
If you notice any signs of folliculitis in your dog, it's essential to seek veterinary attention promptly. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and causing more discomfort for your furry friend.
Common Causes of Folliculitis in Dogs:
- Poor hygiene or grooming practices
- Bacterial or fungal infections
- Allergies to certain substances
- Parasites, such as fleas or mites
Potential Complications of Untreated Folliculitis in Dogs
If left untreated, folliculitis can lead to several complications for dogs. The constant itching and scratching can cause the skin to become more inflamed and irritated. This can result in the formation of painful sores or ulcers on the skin. Additionally, the bacteria or fungi causing the folliculitis can spread to other areas of the body, leading to a more widespread infection.
In severe cases, untreated folliculitis can also weaken the dog's immune system and make them more susceptible to other health issues. It is essential to address folliculitis promptly to prevent these complications from occurring.
Potential Complications of Untreated Folliculitis:
- Formation of painful sores or ulcers on the skin
- Spread of infection to other areas of the body
- Weakened immune system
- Increased susceptibility to other health issues
Diagnosing Folliculitis in Dogs: Methods Used by Veterinarians
Veterinarians use various methods to diagnose folliculitis in dogs. They will typically start by examining the affected areas of the dog's skin and looking for signs of inflammation, redness, or pustules. In some cases, they may need to take a skin scraping or sample to analyze under a microscope or send it to a laboratory for further testing.
In certain situations, veterinarians may also perform additional tests, such as bacterial or fungal cultures, to identify the specific cause of the folliculitis. These diagnostic methods help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for the dog.
Methods Used by Veterinarians to Diagnose Folliculitis:
- Physical examination of the affected areas
- Skin scrapings or samples for microscopic analysis
- Bacterial or fungal cultures
- Allergy testing (if allergies are suspected)
Treatment Options for Folliculitis in Dogs and Expected Recovery Time
The treatment options for folliculitis in dogs depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In mild cases, regular bathing with a medicated shampoo and keeping the affected areas clean and dry may be sufficient. However, if there is an infection present, veterinarians may prescribe oral antibiotics or antifungal medications.
The expected recovery time for dogs with folliculitis can vary depending on several factors, including the dog's overall health and how early treatment was initiated. With proper care and treatment, most dogs show improvement within a few weeks. However, it's crucial to follow your veterinarian's instructions carefully and complete the full course of medication to ensure a successful recovery.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis:
- Regular bathing with medicated shampoo
- Keeping affected areas clean and dry
- Oral antibiotics or antifungal medications
- Topical creams or ointments (in some cases)
Preventive Measures to Reduce the Risk of Folliculitis in Dogs
Preventing folliculitis in dogs involves maintaining good hygiene and taking certain precautions. Regular bathing and grooming help keep their skin clean and reduce the risk of infections. It's essential to use appropriate grooming products that are suitable for a dog's specific needs and avoid any known allergens.
Additionally, preventing flea infestations through regular use of flea preventatives can also help reduce the risk of folliculitis caused by parasites. If your dog has any underlying health conditions or allergies, it's crucial to manage them properly to minimize the chances of developing folliculitis.
Preventive Measures for Folliculitis:
- Regular bathing and grooming
- Using appropriate grooming products
- Avoiding known allergens
- Regular use of flea preventatives
- Managing underlying health conditions or allergies
In conclusion, folliculitis is a skin condition that can affect dogs. It causes irritation and infection in the hair follicles, leading to red bumps and itching. With proper care and treatment from a veterinarian, dogs with folliculitis can recover and have healthy skin again.
What does folliculitis look like on a dog?
Bacterial folliculitis starts off as flat red circles on a dog's skin, known as macules. These macules then develop into raised bumps called papules. In some cases, the papules can fill with pus, resulting in a small white dot in the center of the raised red circle. This description was given on January 9, 2023.
How did my dog get folliculitis?
Folliculitis in dogs occurs when one or multiple hair follicles become irritated due to various conditions, including bacterial infections (often caused by Staphylococcus bacteria), fungal infections (such as ringworm), and parasites (like fleas, ticks, or mites).
Is folliculitis in dogs painful?
According to Dr. McCullough, there are limited methods available to prevent folliculitis. It is advised to follow your veterinarian's guidance in managing any underlying medical issues that could increase the likelihood of your pet developing folliculitis. This condition can be uncomfortable and painful for dogs.
Can Apple cider vinegar help folliculitis in dogs?
Just to be clear, it is not recommended to use apple cider vinegar for treating folliculitis in dogs or pyoderma. It will not be effective and could potentially worsen the condition. There is no scientific evidence or research supporting the idea that apple cider vinegar works for pyoderma or folliculitis.
How do you get rid of folliculitis in dogs?
There are various methods for treating folliculitis in dogs, and the specific treatment will depend on the diagnosis provided by your veterinarian. Antibiotics are commonly used to address bacterial skin infections that lead to folliculitis. In addition, topical medications and ointments can help alleviate skin inflammation. In some cases, your dog may need to take oral antibiotics to effectively treat the condition.
Is dog folliculitis contagious?
Whether or not skin conditions can be transmitted to humans depends on the specific situation. According to Greenstein, skin conditions caused by allergies or other medical issues typically only affect the skin of the affected pet. However, there is a possibility that certain parasitic or fungal infections could potentially be transmitted to humans, although this is uncommon. The statement was made on April 25, 2023.