Key Takeaways:
- Acetaminophen can be toxic to dogs and should not be given without veterinary guidance.
- Even small doses of acetaminophen can cause liver damage in dogs.
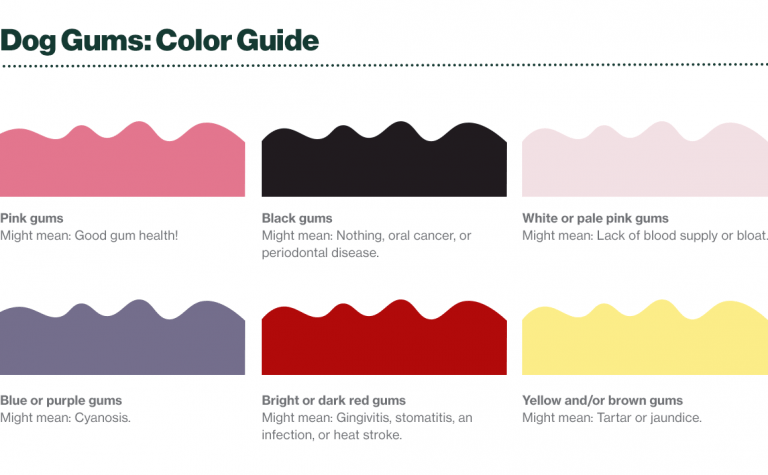
- Symptoms of acetaminophen toxicity in dogs include vomiting, lethargy, difficulty breathing, and brown gums.
- There are safer alternatives for pain relief in dogs, such as medications specifically formulated for canine use.
- If you suspect your dog has ingested acetaminophen, seek immediate veterinary care to prevent serious health complications.
Are you a proud dog owner who wants to ensure the safety and well-being of your furry friend? If so, then understanding whether acetaminophen is safe for dogs is crucial. This topic holds immense value as it can potentially save your dog from unnecessary harm or even a life-threatening situation. By delving into this subject, you will gain the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your dog's health. So, let's explore the world of acetaminophen and its impact on our beloved canine companions. Get ready to uncover the truth behind this commonly used medication and discover how it could affect your furry friend's health. Don't miss out on this essential information that could be a game-changer for your pet's well-being!
What is Acetaminophen and Why Do People Use It?
Acetaminophen is a common pain reliever and fever reducer that many people use to alleviate mild to moderate discomfort. It is available over-the-counter and can be found in various forms such as tablets, capsules, and liquid. Acetaminophen works by blocking certain chemicals in the brain that cause pain and fever.
People use acetaminophen for various reasons, including headaches, muscle aches, toothaches, menstrual cramps, and minor injuries. It is also commonly used to reduce fever associated with illnesses like the flu or colds. Acetaminophen is considered safe when used as directed and can provide effective relief for many individuals.
Why do people choose acetaminophen?
One of the main reasons people choose acetaminophen is because it is easily accessible without a prescription. This means that it can be conveniently purchased at most pharmacies or grocery stores without needing to visit a doctor. Additionally, acetaminophen has been widely used for many years and has a long-standing reputation for safety when taken correctly.
Another advantage of acetaminophen is its versatility in treating different types of pain. Whether it's a headache from stress or a sprained ankle from playing sports, acetaminophen can help provide relief. Its ability to reduce fever also makes it beneficial for managing symptoms during illness.
Listed below are some common uses of acetaminophen:
- Pain relief: Headaches, muscle aches, toothaches
- Fever reduction: Associated with flu or colds
- Menstrual cramp relief
- Minor injury pain management
Is Acetaminophen Safe for Dogs Like Humans?
When it comes to giving acetaminophen to dogs, it is important to understand that what may be safe for humans can be dangerous for our furry friends. While acetaminophen is commonly used by humans to relieve pain and reduce fever, it can have harmful effects on dogs. Dogs lack a specific enzyme called glucuronyl transferase, which helps break down and eliminate acetaminophen from the body. As a result, even small doses of acetaminophen can lead to toxicity in dogs.
The Dangers of Acetaminophen for Dogs
Acetaminophen can cause damage to a dog's liver and red blood cells. It can also affect their ability to transport oxygen throughout the body, leading to serious health complications. Symptoms of acetaminophen toxicity in dogs include vomiting, loss of appetite, lethargy, difficulty breathing, and even collapse. If you suspect your dog has ingested acetaminophen or is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate veterinary care.
Safe Pain Relief Options for Dogs
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications are commonly prescribed by veterinarians for pain relief in dogs. Examples include carprofen and meloxicam.
- Opioids: In certain cases where stronger pain relief is necessary, opioids may be prescribed by a veterinarian. However, these medications should only be used under close veterinary supervision due to their potential side effects.
- Natural remedies: Some natural supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can help alleviate joint pain in dogs. However, it's important to consult with a veterinarian before starting any new supplements.
Risks and Side Effects of Acetaminophen for Dogs
Acetaminophen can have severe risks and side effects when given to dogs. One of the most significant risks is liver damage. Dogs lack the necessary enzymes to metabolize acetaminophen efficiently, leading to the accumulation of toxic byproducts in their liver. This can result in liver failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
Recognizing the Side Effects
The side effects of acetaminophen toxicity in dogs can vary depending on the dosage ingested and the individual dog's sensitivity. Common symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, and even coma. It's crucial to monitor your dog closely if they have accidentally consumed acetaminophen or if you suspect any adverse reactions.
Immediate Veterinary Care
If you believe your dog has ingested acetaminophen or is experiencing any symptoms of toxicity, it is essential to seek immediate veterinary care. Time is of the essence when dealing with potential poisoning cases, as early intervention can greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome. Your veterinarian will be able to assess your dog's condition and provide appropriate treatment options.
How Does Acetaminophen Affect a Dog's Body Compared to Humans?
Metabolism Differences
Acetaminophen, commonly known as Tylenol, affects dogs and humans differently due to variations in metabolism. Dogs have a limited ability to metabolize acetaminophen compared to humans. While humans can efficiently break down acetaminophen into harmless byproducts, dogs lack certain liver enzymes necessary for this process. As a result, the drug can accumulate in their system and cause toxicity.
Toxicity Symptoms
When dogs ingest acetaminophen, they may experience symptoms such as vomiting, loss of appetite, lethargy, abdominal pain, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, it can lead to liver damage or even death. It is crucial for dog owners to be aware of these symptoms and seek immediate veterinary care if their pet shows any signs of acetaminophen poisoning.
Preventing Accidental Ingestion
To prevent accidental ingestion of acetaminophen by dogs, it is essential to store medications securely out of their reach. Dogs are curious creatures and may accidentally consume pills left within their access. Additionally, never administer human medications to dogs without veterinary guidance.
Safe Alternatives to Acetaminophen for Dog Pain Relief
Veterinary-Approved Pain Medications
When it comes to managing pain in dogs, there are several safe alternatives to acetaminophen that veterinarians may prescribe. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) specifically formulated for canine use are commonly recommended. These medications help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation without posing the same risks as acetaminophen.
Natural Remedies
In addition to prescribed medications, there are also natural remedies that can provide relief for dog pain. These include supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin, which support joint health, as well as herbal remedies such as turmeric or fish oil. However, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian before administering any natural remedies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your dog.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and physical therapy can also play a significant role in managing pain in dogs. Low-impact activities like swimming or controlled walks can help improve muscle strength, joint mobility, and overall well-being. It is important to work closely with a veterinarian or a certified canine rehabilitation therapist to develop an appropriate exercise plan tailored to your dog's specific needs.
Ensuring the Safety of Your Dog When Giving Medications
Consulting a Veterinarian
Before giving any medication to your dog, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian. They have the expertise to determine the right dosage and recommend suitable medications based on your dog's condition. Never assume that human medications can be directly given to dogs without professional guidance.
Proper Administration Techniques
When administering medications at home, it is important to follow proper techniques to ensure your dog's safety. This may involve using pill pockets or hiding medication in food to make it more palatable for your pet. Always read the instructions carefully and avoid crushing or splitting tablets unless specifically instructed by your veterinarian.
Monitoring for Side Effects
After giving medication to your dog, closely monitor them for any potential side effects. If you notice any unusual behavior or symptoms after administering a medication, contact your veterinarian immediately. Prompt communication with your vet can help address any concerns and ensure the ongoing safety of your furry companion.
Remember, when it comes to managing pain or providing any form of medical treatment for dogs, always prioritize professional veterinary advice. Your veterinarian is the best resource to guide you in making informed decisions for your dog's health and well-being.
In conclusion, acetaminophen is not safe for dogs. It can be toxic and cause serious harm to their liver and other organs. It is best to consult a veterinarian for appropriate pain relief options for our furry friends.
Is 500mg of acetaminophen safe for dogs?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is highly toxic to dogs and cats, and even small doses, such as a single pill or a small piece of a pill, can be lethal to various animal species including cats, dogs, ferrets, birds, pigs, primates, and more.
What type of painkiller is safe for dogs?
The FDA has approved several NSAIDs for pets, including carprofen, deracoxib, firocoxib, and grapiprant. These medications are specifically for dogs and are available under various brand and generic names.
Can I give my dog acetaminophen for pain relief?
There are significant differences in metabolism between humans and dogs. This means that certain medications that are safe for humans can be harmful or even fatal for dogs. It is important to never give your dog common over-the-counter pain relievers such as Acetaminophen (Tylenol).
How much acetaminophen is safe for a dog?
What is the recommended dosage of Tylenol for dogs? It is typically recommended to give dogs 5 to 7 mg of Tylenol per pound of body weight twice a day.
What happens if a dog eats 1 Tylenol?
What are the symptoms of acetaminophen poisoning in dogs? Symptoms of acetaminophen poisoning can occur within 1-4 hours of ingestion. Affected dogs will show signs of increasing lethargy and may experience rapid breathing. They can also have abdominal discomfort and nausea, which may lead to excessive drooling.
What happens if my dog eats half a Tylenol 500 mg tablet?
Regrettably, dogs are susceptible to the toxicity of acetaminophen. This substance can harm the liver and impair the ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen, resulting in a condition known as methemoglobinemia.