Key Takeaways:
- Possessive aggression in dogs is often caused by fear or insecurity, as they feel the need to protect their resources.
- It is important to identify triggers that lead to possessive aggression, such as food, toys, or specific areas.
- Proper training and socialization from an early age can help prevent possessive aggression in dogs.
- Using positive reinforcement techniques and rewarding good behavior can be effective in stopping possessive aggression.
- Consulting with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist may be necessary for severe cases of possessive aggression in dogs.
Are you a dog lover? Do you want to understand why some dogs become possessive and aggressive? If so, get ready to unlock the secrets behind this behavior and discover how to put an end to it. Understanding the reasons for possessive aggression in dogs is not only fascinating but also essential for responsible pet ownership. By delving into this topic, you will gain valuable insights that can help create a harmonious relationship with your furry friend. So, let's embark on this journey together as we explore the fascinating world of possessive aggression in dogs and learn effective strategies to stop it once and for all. Get ready to unleash a happier, healthier bond with your four-legged companion!
Why do some dogs become possessively aggressive?
When a dog becomes possessively aggressive, it means that they show aggression when they feel like something they value is being taken away from them. This behavior can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as fear, insecurity, or a lack of proper socialization and training. Dogs may also develop possessive aggression if they have had negative experiences in the past where their resources were threatened or taken away.
Possessive aggression can manifest in different ways, depending on the individual dog. Some dogs may growl, snarl, or snap at people or other animals who approach their possessions. They may also guard their food bowls, toys, or even their favorite spots on the couch. It's important to understand that possessive aggression is not a sign of dominance but rather a defensive reaction to protect what the dog considers valuable.
Common signs of possessive aggression in dogs
- Growling or snarling when someone approaches their possessions
- Biting or snapping at people or other animals who come near their belongings
- Guarding food bowls, toys, beds, or other resources
- Showing stiff body language and raised hackles when someone tries to take something away
The harmful effects of a dog's possessive aggression
Possessive aggression in dogs can have serious consequences for both the dog and those around them. If not addressed and managed properly, it can lead to injuries for humans and other pets. It can also strain relationships between the dog and its family members, causing stress and anxiety for everyone involved.
In extreme cases, possessive aggression can result in legal issues if the dog causes harm to someone. This could lead to the dog being taken away or even euthanized. It is crucial to address possessive aggression early on to prevent these negative outcomes and ensure the well-being of both the dog and its environment.
Possible triggers for possessive aggression in dogs
There are several factors that can contribute to a dog developing possessive aggression. These include:
- Lack of proper socialization during puppyhood, which can make a dog more fearful and reactive
- Past experiences where their resources were threatened or taken away
- Inconsistent or inadequate training, leading to confusion about boundaries and acceptable behavior
- Genetic predisposition towards guarding behaviors
- Anxiety or fear-related issues that manifest as possessive aggression
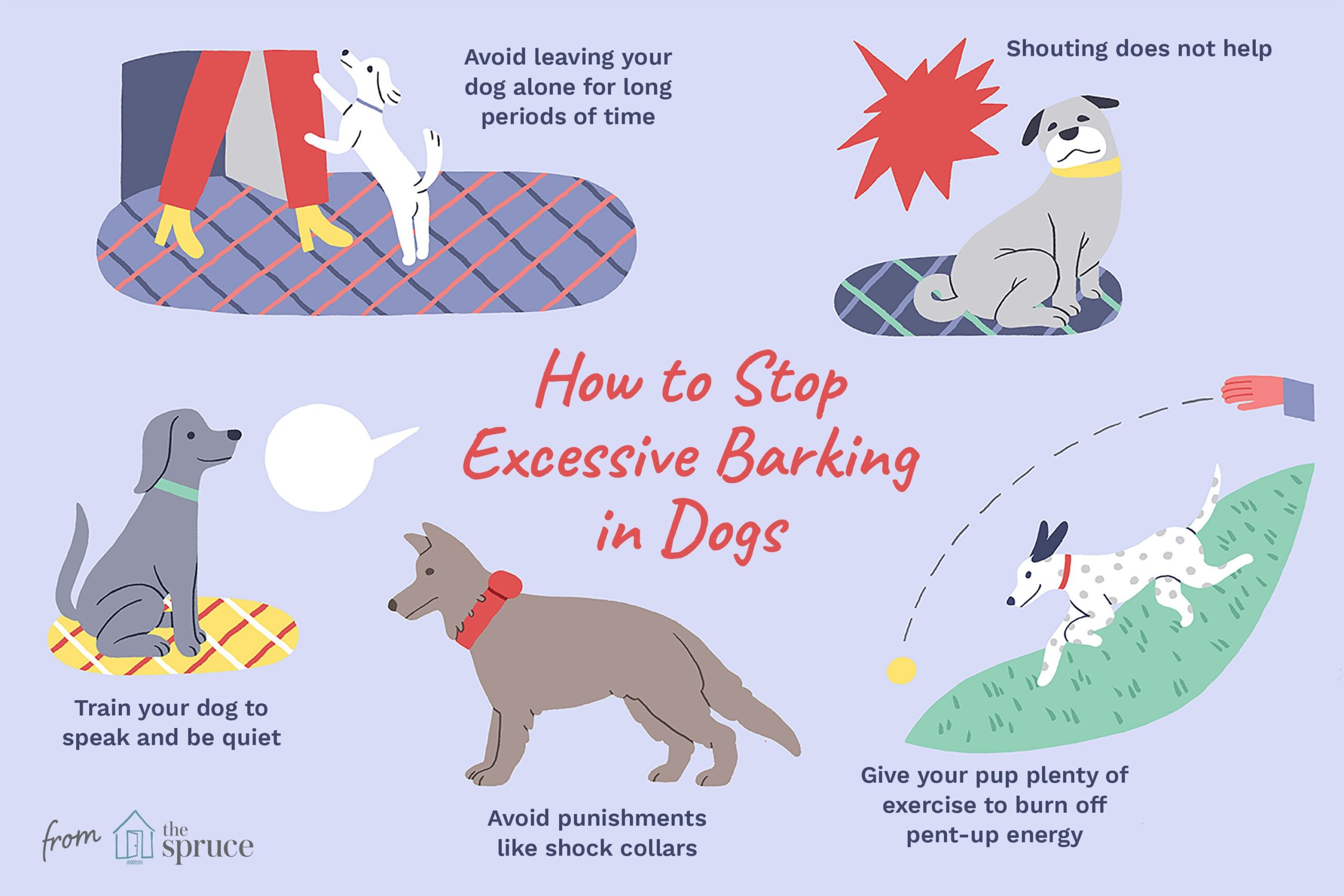
Effective strategies to prevent or stop possessive aggression in dogs
Dealing with possessive aggression requires a combination of management, training, and behavior modification techniques. Here are some effective strategies:
- Provide proper socialization from an early age to help your dog feel more comfortable and confident in various situations.
- Teach your dog basic obedience commands like "sit," "stay," and "drop it" so they understand and respect your authority.
- Avoid situations that trigger possessive behavior whenever possible, but if they do occur, use positive reinforcement techniques to redirect your dog's attention.
- Consult with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist who can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
- Consider using desensitization and counterconditioning exercises to change your dog's emotional response to situations that trigger possessiveness.
Reducing possessive aggression through training and socialization
Training and socialization play a crucial role in reducing possessive aggression in dogs. By teaching your dog appropriate behaviors and exposing them to different environments, you can help them become more confident and less reactive.
Positive reinforcement training methods, such as rewarding good behavior with treats or praise, are highly effective in shaping your dog's behavior. Consistency is key, so be patient and persistent in your training efforts.
Professional resources for dealing with possessive aggression in dogs
If you're struggling to manage your dog's possessive aggression on your own, it can be beneficial to seek professional help. A certified dog trainer or a veterinary behaviorist can provide expert guidance tailored to your specific situation.
These professionals have extensive experience working with aggressive dogs and can create a customized training plan that addresses the root causes of possessive aggression. They will also teach you techniques to manage the behavior effectively and ensure the safety of everyone involved.
Common signs of possessive aggression in dogs
Growling and Snapping
One common sign of possessive aggression in dogs is growling and snapping when someone or another animal approaches their food, toys, or other possessions. This behavior is a way for the dog to assert dominance and protect what they perceive as theirs.
Guarding Behavior
Another sign of possessive aggression is guarding behavior. Dogs may become overly protective of their belongings and exhibit aggressive behavior when someone tries to take them away. They may show signs of tension, such as stiffening their body, staring intensely, or even lunging at the person or animal who poses a threat to their possessions.
Resource Guarding
Resource guarding is a specific type of possessive aggression where dogs become defensive over valuable resources like food, bones, or favorite toys. They may growl, snap, or bite if someone tries to approach while they are consuming these items.
It's important to note that possessive aggression can vary in intensity from mild warning signals to more severe aggressive behaviors. Recognizing these signs early on can help prevent potential conflicts and ensure the safety of both humans and animals involved.
The harmful effects of a dog's possessive aggression
Possessive aggression in dogs can have several harmful effects on both the dog itself and those around it.
Risk of Injury
When a dog displays possessive aggression, there is an increased risk of injury to humans or other animals. The dog may bite or attack if they feel threatened or believe their possessions are being taken away. This can result in serious injuries that require medical attention.
Strained Relationships
Possessive aggression can strain relationships between the dog and its owners, as well as with other family members or pets in the household. The constant tension and fear of aggression can lead to a breakdown in trust and create a stressful environment for everyone involved.
Isolation
In some cases, dogs with possessive aggression may need to be isolated from certain situations or environments to prevent potential conflicts. This isolation can limit their social interactions and negatively impact their overall well-being.
It is crucial to address possessive aggression in dogs promptly to minimize these harmful effects and ensure a safe and harmonious living environment for both the dog and its human companions.
Possible triggers for possessive aggression in dogs
1. Resource Guarding
Resource guarding is a common trigger for possessive aggression in dogs. This occurs when a dog becomes overly protective of their possessions, such as food, toys, or even their favorite spot on the couch. When someone or another animal approaches these items, the dog may display aggressive behaviors like growling or snapping.
2. Fear and Insecurity
Fear and insecurity can also contribute to possessive aggression in dogs. If a dog feels threatened or anxious, they may become possessive over certain objects as a way to cope with their fear. This behavior is often seen in rescue dogs who have experienced trauma or neglect in the past.
Signs of Possessive Aggression:
- Growling or snarling when approached near possessions
- Stiff body posture and raised hackles
- Lunging or biting to protect resources
- Intense staring and showing teeth
It's important to note that possessive aggression is not always predictable and can vary from dog to dog. Understanding these triggers can help owners identify potential situations that may lead to possessive aggression and take appropriate measures to prevent it.
Effective strategies to prevent or stop possessive aggression in dogs
1. Avoid Provoking Possessiveness
One effective strategy is to avoid provoking possessiveness in your dog by not approaching them while they are eating or playing with their toys. Respect their personal space during these times, which will help them feel more secure and less likely to exhibit aggressive behaviors.
2. Positive Reinforcement Training
Positive reinforcement training is an excellent approach for addressing possessive aggression. By rewarding your dog for calm behavior around resources and teaching them cues like "drop it" or "leave it," you can gradually reduce their possessive tendencies. Consistency and patience are key in this training process.
Tips for Training:
- Use high-value treats or rewards to motivate your dog during training sessions.
- Start with less valuable items and gradually work up to more prized possessions.
- Seek professional guidance if your dog's possessive aggression persists or worsens.
Remember, punishment-based methods can escalate possessive aggression and should be avoided. Instead, focus on positive reinforcement techniques that promote trust and cooperation between you and your furry friend.
Reducing possessive aggression through training and socialization
1. Early Socialization
Early socialization plays a crucial role in reducing possessive aggression in dogs. Exposing them to various people, animals, and environments from a young age helps them develop confidence and adaptability. This exposure should include positive interactions with other dogs while sharing toys or resources.
2. Controlled Desensitization
Controlled desensitization is another effective technique for reducing possessive aggression. Gradually exposing your dog to situations that trigger possessiveness, such as having someone approach their food bowl while they eat, can help them learn that these situations are not threatening. Start with minimal distractions and gradually increase the difficulty level as your dog becomes more comfortable.
Benefits of Training and Socialization:
- Builds trust between the dog and owner
- Enhances the dog's ability to handle stressful situations
- Reduces the likelihood of possessive aggression towards both humans and other animals
By incorporating consistent training and socialization into your dog's routine, you can significantly decrease their tendency towards possessive aggression over time.
Professional resources for dealing with possessive aggression in dogs
1. Certified Dog Trainers
Certified dog trainers specialize in behavior modification and can provide personalized guidance for dealing with possessive aggression. They will assess your dog's specific needs and create a training plan tailored to address their possessiveness effectively.
2. Animal Behaviorists
Animal behaviorists are experts in understanding the psychological aspects of animal behavior. They can help identify the underlying causes of possessive aggression in dogs and develop comprehensive treatment plans that may include behavior modification techniques, medication if necessary, and ongoing support.
Benefits of Professional Assistance:
- Expert knowledge and experience in dealing with possessive aggression
- Customized strategies based on your dog's unique situation
- Ongoing support throughout the training process
Seeking professional resources is highly recommended, especially if your dog's possessive aggression poses a risk to their safety or the well-being of others. Remember, addressing this issue promptly can lead to a happier and more harmonious relationship between you and your furry companion.
In conclusion, possessive aggression in dogs can be caused by fear or insecurity, and it is important to address this behavior to ensure everyone's safety. By seeking professional help, training your dog with positive reinforcement, and providing a secure environment, you can help stop possessive aggression in your furry friend.
How do you fix possessive aggression in dogs?
The objective is to train the dog by providing a highly desirable treat or reward that is more attractive than the item it currently has. By approaching calmly, offering a food reward, taking the possession, praising the puppy, and returning the object, the puppy learns that your actions are not something to be afraid of.
How do I get my dog to stop being so possessive?
"Dropping it" is a crucial command for all dogs, particularly for those who tend to become possessive over toys. Teaching your dog to reliably "drop it" can prevent possessive behavior from occurring. Another related command is "trade ya," which can be useful if your dog is reluctant to let go of something they are guarding.
What makes a dog possessive aggressive?
Dogs that have been stray or had the freedom to roam may develop possessive aggression as a way to survive. If puppies with these traits are not properly trained, it can reinforce their possessive behavior and their aggression can become worse as they grow older.
How do you break possessive aggression?
Rather than removing your dog's prized possession, consider introducing something that your dog may find even more valuable, such as a special treat or a new toy. If your dog is holding onto the item they are guarding, you can use the command "drop it" to encourage them to let go. Just ensure that you have a rewarding incentive.
Do dogs grow out of dominance aggression?
Certain puppies may exhibit dominant behaviors from an early age, while others may not display signs of dominance until they are fully grown. Dealing with aggression stemming from dominance can be challenging and requires consistent effort and a significant amount of time.
What is a possessive dog behavior over owner?
Regardless of the situation, when your dog behaves in this way, they are attempting to communicate to you that something belongs to them and you should find your own. A possessive dog is seeking to establish dominance and control. They may assert ownership over their toys, food bowl, sleeping space, or even their owner. They might growl at you if you try to approach their food bowl, regardless of whether it contains food or not.