Key Takeaways:
- Senior dogs are more prone to developing dementia as they age.
- Dementia in dogs can cause changes in behavior, such as confusion and disorientation.
- Providing a consistent routine and environment can help manage symptoms of dementia in senior dogs.
- Medications and supplements may be prescribed by a veterinarian to slow down the progression of dementia in dogs.
- Regular veterinary check-ups are important for early detection and management of dementia in senior dogs.
Welcome to a fascinating journey into the world of senior dementia in dogs, where we uncover the hidden secrets behind their aging minds. By exploring this topic, you will gain invaluable insights into understanding and caring for our furry friends in their twilight years.
Imagine being able to decode the mysteries of your beloved pet's behavior and provide them with the support they need during this challenging phase of life. Understanding senior dementia in dogs is not just essential for their well-being but also for strengthening the bond between you and your furry companion.
Understanding Senior Dementia in Dogs: What You Need to Know
Dementia is a condition that affects the brain and can occur in older dogs, just like it does in humans. As dogs age, their brain function may decline, leading to changes in behavior and cognitive abilities. It's important for dog owners to understand senior dementia so they can provide the best care for their furry friends.
Senior dementia in dogs is also known as canine cognitive dysfunction (CCD). It is a progressive condition that worsens over time and can have a significant impact on a dog's quality of life. While the exact cause of CCD is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to changes in the brain, including the accumulation of abnormal proteins.
Causes of Senior Dementia in Dogs
The exact causes of senior dementia in dogs are not known, but there are several factors that may contribute to its development:
- Age: Older dogs are more likely to develop dementia than younger ones.
- Genetics: Some dog breeds may be more predisposed to developing cognitive dysfunction.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor diet, lack of mental stimulation, and limited physical activity may increase the risk of cognitive decline.
Risk Factors for Senior Dementia in Dogs
While any dog can develop senior dementia, certain factors may increase their risk:
- Age: Dogs over the age of 10 are more susceptible to developing cognitive dysfunction.
- Breed: Certain breeds, such as Labrador Retrievers and Golden Retrievers, may have a higher predisposition to CCD.
- Poor health: Dogs with underlying medical conditions or chronic illnesses may be more prone to developing dementia.
Diagnosing Senior Dementia in Dogs
Diagnosing senior dementia in dogs can be challenging, as there is no definitive test for CCD. However, a veterinarian will typically perform a thorough physical examination and evaluate the dog's medical history and behavior changes. They may also rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as thyroid or metabolic disorders.
In some cases, additional tests like blood work or imaging studies may be recommended to rule out other potential causes or to assess the overall health of the dog. It's important to consult with a veterinarian if you suspect your older dog may be experiencing cognitive decline.
Recognizing the Signs of Senior Dementia in Your Older Dog
Changes in Behavior
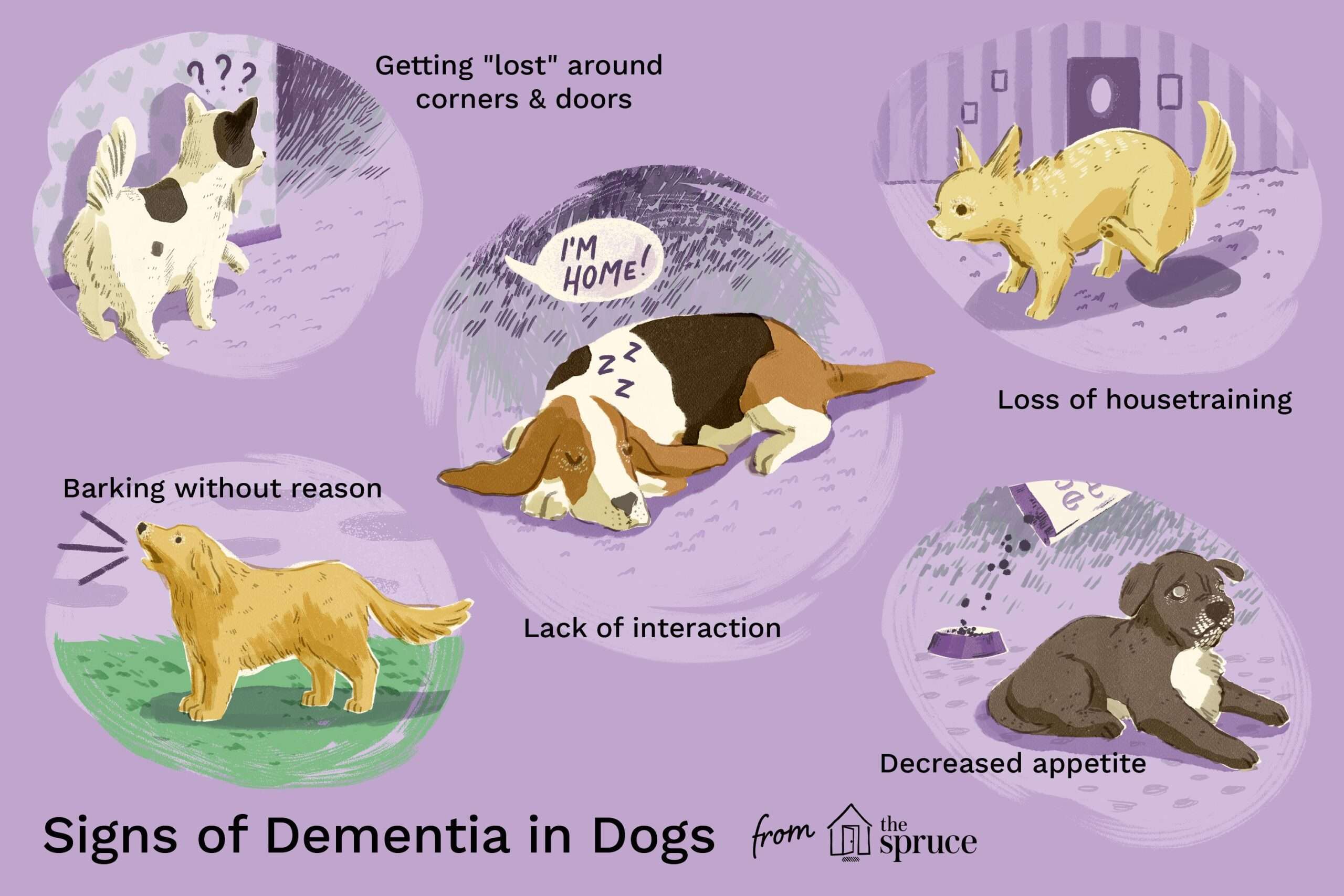
As dogs age, it is important to pay attention to any changes in their behavior. One of the first signs of senior dementia in dogs is a change in their normal behavior patterns. They may become more anxious or restless, or they may start to withdraw and become less interested in activities they used to enjoy. They may also exhibit confusion or disorientation, such as getting lost in familiar places or forgetting commands they once knew.
Problems with Memory and Learning
Another common sign of senior dementia in dogs is a decline in memory and learning abilities. Your dog may have difficulty remembering familiar people or places, and they may struggle with basic commands that they previously knew well. They may also have trouble learning new tasks or following routines that were once second nature to them.
Physical Symptoms
In addition to changes in behavior and cognitive abilities, senior dogs with dementia may also experience physical symptoms. These can include increased accidents indoors due to difficulty controlling their bladder or bowels, changes in appetite or weight loss, sleep disturbances, and even changes in their sense of smell or hearing.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other health issues, so it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis.
Common Symptoms of Senior Dementia in Dogs: What to Look Out For
Sundowning Behavior
Sundowning behavior refers to a phenomenon where dogs with senior dementia become more agitated or confused during the evening hours. This can manifest as restlessness, pacing, barking for no apparent reason, or increased anxiety as the sun sets. It is believed that this behavior occurs due to disruptions in the dog's internal clock caused by brain changes associated with dementia.
Loss of Interest in Social Interaction
Senior dogs with dementia may also exhibit a loss of interest in social interaction. They may no longer greet family members or show excitement when visitors arrive. They may prefer to spend more time alone and avoid interactions with other pets or family members. This withdrawal from social interaction can be distressing for both the dog and their owners.
Increased Irritability
Another symptom to look out for is increased irritability. Dogs with senior dementia may become easily agitated or snap at people or other animals without provocation. This change in temperament can be challenging to manage and may require additional patience and understanding from their owners.
By recognizing these common symptoms, you can better understand if your older dog is experiencing senior dementia and take appropriate steps to provide them with the care they need.
Managing Senior Dementia in Dogs: Treatment and Medication Options
Environmental Enrichment
One approach to managing senior dementia in dogs is through environmental enrichment. Providing mental stimulation through interactive toys, puzzles, and games can help keep their minds active and engaged. Creating a safe space where they feel comfortable and secure is also important, as it can reduce anxiety and confusion.
Dietary Changes
Adjusting your dog's diet can also play a role in managing senior dementia. Certain nutrients, such as antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, have been shown to support brain health in aging dogs. Consult with your veterinarian about incorporating these nutrients into your dog's diet through specialized senior dog food or supplements.
Medication Options
In some cases, medication may be prescribed by a veterinarian to help manage the symptoms of senior dementia in dogs. These medications aim to improve cognitive function, reduce anxiety, or alleviate other related symptoms. It is important to follow your veterinarian's guidance and closely monitor your dog's response to the medication.
By implementing these management strategies, you can help improve your dog's quality of life and slow down the progression of senior dementia.
Benefits of Changes in Diet and Exercise for Dogs with Senior Dementia
Promotes Brain Health
Making changes to your older dog's diet and exercise routine can have significant benefits for their brain health. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports cognitive function and helps reduce inflammation in the brain. Regular exercise stimulates blood flow to the brain, promoting mental sharpness and overall well-being.
Manages Weight and Muscle Tone
As dogs age, they may become less active, leading to weight gain and muscle loss. By adjusting their diet and exercise regimen, you can help manage their weight and maintain muscle tone. This not only improves their physical health but also contributes to better cognitive function by reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions that can impact brain health.
Enhances Overall Well-being
Changes in diet and exercise not only benefit a dog's physical health but also contribute to their overall well-being. Regular exercise provides mental stimulation, reduces stress levels, promotes better sleep patterns, and enhances mood. A nutritious diet supports optimal body function, which positively impacts a dog's energy levels and vitality.
By incorporating appropriate dietary changes and regular exercise into your older dog's routine, you can support their brain health while improving their overall quality of life.
Creating a Safe and Comfortable Environment for a Dog with Senior Dementia at Home
Minimizing Hazards
Creating a safe environment is crucial for dogs with senior dementia as they may experience difficulties navigating their surroundings. Remove any potential hazards such as loose rugs or cluttered pathways that could cause them to trip or fall. Install baby gates or use barriers to restrict access to areas that may pose risks, such as staircases or swimming pools.
Establishing Routine and Familiarity
Maintaining a consistent routine can help dogs with senior dementia feel more secure and reduce anxiety. Stick to regular feeding times, exercise schedules, and bedtime routines. Keep their belongings, such as their bed and favorite toys, in familiar locations to provide a sense of comfort and familiarity.
Providing Comfortable Rest Areas
Senior dogs with dementia may require additional rest throughout the day. Create comfortable resting areas where they can relax undisturbed. Provide soft bedding that supports their joints and consider using calming aids, such as pheromone diffusers or soothing music, to create a peaceful environment.
By implementing these measures, you can ensure your dog's safety and create a comforting environment that promotes their well-being despite the challenges of senior dementia.
Preventing or Delaying the Onset of Senior Dementia in Dogs: Strategies to Consider
Mental Stimulation Activities
Engaging your dog in mental stimulation activities from an early age can help keep their brain active and potentially delay the onset of senior dementia. Interactive puzzle toys, obedience training sessions, and learning new tricks are all effective ways to challenge their cognitive abilities.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring your dog's overall health and detecting any potential issues early on. Your veterinarian can assess your dog's cognitive function during these visits and provide guidance on preventive measures specific to your dog's breed and age.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle for your dog is crucial in preventing or delaying the onset of senior dementia. This includes providing a balanced diet tailored to their nutritional needs, regular exercise appropriate for their age and breed, and ensuring they receive proper dental care. Avoiding exposure to toxins and maintaining a stress-free environment also contribute to their overall well-being.
By implementing these preventive strategies, you can help promote your dog's brain health and potentially delay the onset of senior dementia, allowing them to enjoy a longer and healthier life.
In conclusion, senior dementia in dogs is a condition that affects older dogs and can cause memory loss and confusion. It is important for dog owners to recognize the signs and provide proper care and support for their furry friends as they age.
How long can a senior dog live with dementia?
On average, dogs with dementia can live for approximately two years after being officially diagnosed. However, the length of time can vary depending on the dog's overall physical and mental well-being, the speed at which the disease advances, and how early the symptoms of dementia were detected.
How do I know if my senior dog has dementia?
Dogs suffering from CCD (Canine Cognitive Dysfunction) often experience confusion, particularly within familiar surroundings such as their own homes. They may struggle to locate their food bowls or navigate between different levels of the house. As the disorder progresses, they may even forget their own name or fail to recognize their own family members. Changes in sleep patterns are also common symptoms.
What are the last stages of dementia in a dog?
In the final stage, the symptoms mentioned earlier become more severe. Additionally, your dog may exhibit increased nighttime wandering instead of sleeping and may start barking at imaginary things.
How do I know if my dog with dementia is suffering?
The following are the typical signs of dog dementia: Disorientation and confusion - Acting lost or disoriented in familiar surroundings. Anxiety. Forgetting daily routines and previously learned training or house rules.
Can dog dementia get worse suddenly?
While the initial symptoms of the disorder are not severe, they gradually deteriorate over time, surpassing what is typically seen in normal aging. These animals undergo a process called "cognitive decline" where their brain's ability to carry out regular tasks gradually diminishes.
When should you euthanize a dog with dementia?
Deciding when to euthanize a dog with dementia can be challenging. However, there are certain indications that it may be appropriate, such as a decrease in their quality of life, loss of appetite, inability to manage bodily functions, and heightened confusion and anxiety.