Key Takeaways:
- Spaying is a surgical procedure that involves removing the ovaries and uterus of female dogs.
- It is recommended to spay dogs before their first heat cycle, which usually occurs around 6 months of age.
- Spaying can prevent unwanted litters, reduce the risk of certain diseases like mammary tumors and uterine infections, and eliminate the possibility of uterine or ovarian cancer.
- The procedure is generally safe but requires anesthesia and post-operative care to ensure proper healing.
- Spaying can also have behavioral benefits, such as reducing aggression and roaming tendencies in female dogs.
Are you a dog lover? Do you want to ensure the health and well-being of your furry friend? Then, understanding the procedure of spaying is crucial. This simple yet essential surgery not only prevents unwanted pregnancies but also helps in preventing certain diseases and behavioral problems in dogs. By delving into this topic, you'll gain valuable insights into how spaying can benefit your beloved pet's overall health and happiness. So, let's dive right in and explore all about the procedure of spaying in dogs, ensuring a brighter future for our four-legged companions!
What is Spaying and Why is it Important for Female Dogs?
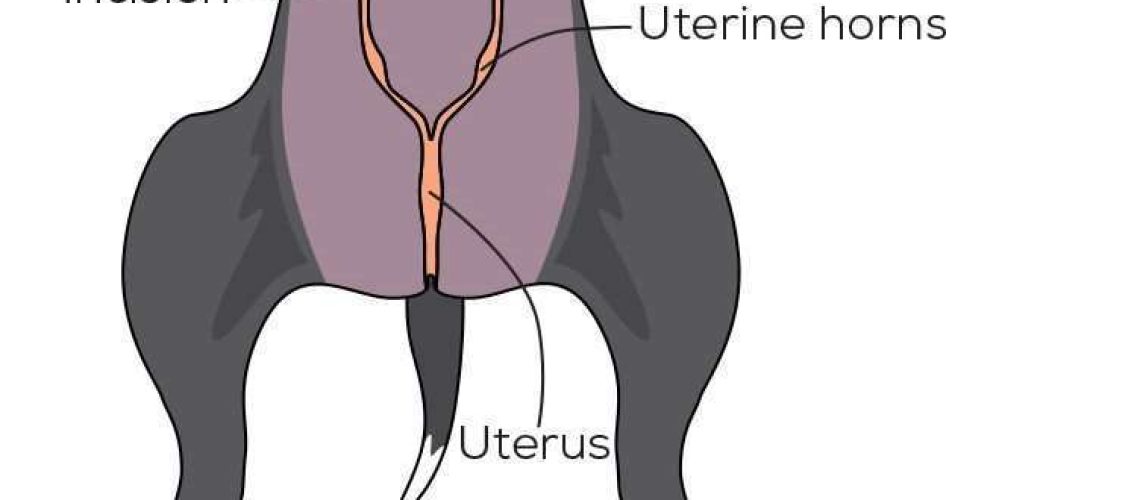
Spaying, also known as ovariohysterectomy, is a surgical procedure performed on female dogs to remove their reproductive organs. This includes the removal of the ovaries and uterus. Spaying is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduces the number of stray dogs in the community. It also eliminates the risk of uterine infections, such as pyometra, which can be life-threatening for dogs. Additionally, spaying can help prevent certain types of cancer that are more common in unspayed female dogs, such as mammary gland tumors.
Benefits of spaying:
- Prevents unwanted pregnancies
- Reduces the risk of uterine infections
- Decreases the chances of certain types of cancer
Why spay your dog?
Spaying your female dog not only benefits her health but also contributes to controlling the pet population. By preventing unplanned litters, you are helping reduce the number of homeless dogs and ensuring that every dog has a loving home. Spaying can also improve your dog's behavior by reducing or eliminating certain hormone-driven behaviors like roaming or aggression.
How is the Spaying Procedure Performed on Dogs?
The spaying procedure involves making an incision in the abdomen to access and remove the reproductive organs. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure that your dog feels no pain during the procedure. Once your dog is asleep, a small incision is made near her belly button to access the uterus and ovaries. The veterinarian carefully removes these organs before closing up the incision with stitches or surgical staples.
The steps involved in spaying:
1. Administering anesthesia: Your dog will be given medication to make her sleep during surgery.
2. Making an incision: The veterinarian will make a small incision near the belly button to access the reproductive organs.
3. Removing the uterus and ovaries: The veterinarian will carefully remove these organs to prevent future pregnancies and eliminate the risk of certain diseases.
4. Closing the incision: The incision is closed using stitches or surgical staples, which will be removed at a later date.
Recovery after spaying:
After the surgery, your dog will need time to recover. It is important to follow your veterinarian's instructions regarding pain medication, activity restrictions, and wound care. Your dog may experience some discomfort or lethargy for a few days following the procedure, but this should improve gradually. It is essential to keep your dog calm and prevent her from licking or scratching at the incision site to avoid infection.
Are There Any Risks or Complications with Dog Spaying?
Like any surgical procedure, spaying does come with some risks and potential complications. However, these risks are generally low, especially when performed by a skilled veterinarian in a proper medical facility. Some possible risks include adverse reactions to anesthesia, infection at the incision site, excessive bleeding during surgery, or accidental damage to surrounding organs.
Reducing risks:
To minimize these risks:
- Choose a reputable veterinary clinic with experienced surgeons.
- Ensure that pre-operative blood work is done to check your dog's overall health before surgery.
- Follow all post-operative care instructions provided by your veterinarian.
It is important to discuss any concerns you have about potential risks with your veterinarian before scheduling the spaying procedure for your dog.
When is the Best Time to Have a Female Dog Spayed?
The ideal time for spaying a female dog can vary depending on factors such as breed, size, and overall health. In general, most veterinarians recommend spaying dogs between the ages of six months to one year. However, some smaller breeds may reach sexual maturity earlier, while larger breeds may take longer.
Factors to consider:
- Breed: Different breeds mature at different rates, so it is important to consult with your veterinarian about the best timing for your specific breed.
- Health: Your dog should be in good overall health before undergoing surgery. It is essential to discuss any existing health conditions or concerns with your veterinarian.
- Heat cycle: Spaying before the first heat cycle can help prevent certain diseases and unwanted pregnancies. However, spaying during or immediately after a heat cycle may increase the risk of complications and make the surgery more challenging.
It is crucial to have a discussion with your veterinarian to determine the best time for spaying based on your individual dog's needs and circumstances.
The Benefits of Spaying a Female Dog: Health and Behavior
Spaying offers numerous benefits for both the health and behavior of female dogs. By removing the reproductive organs, you can help prevent certain diseases and improve your dog's overall well-being. Spayed dogs are less likely to develop mammary gland tumors, uterine infections (pyometra), or ovarian cysts. These conditions can be costly to treat and potentially life-threatening.
Furthermore, spaying can have positive effects on your dog's behavior. It helps reduce hormone-driven behaviors such as roaming in search of mates or aggressive tendencies towards other animals during heat cycles. Spayed dogs also tend to be calmer and less prone to certain types of territorial marking.
Overall, spaying not only provides health benefits but also contributes to a happier and more balanced life for your female dog.
How Does Spaying Help Prevent Diseases in Female Dogs?
Spaying plays a crucial role in preventing various diseases that commonly affect female dogs. Here are some of the diseases that can be prevented or significantly reduced by spaying:
Mammary gland tumors:
Spaying before the first heat cycle greatly reduces the risk of mammary gland tumors, which are often malignant in dogs. The risk increases with each subsequent heat cycle, so early spaying is essential for maximum protection.
Uterine infections (pyometra):
Pyometra is a serious infection of the uterus that primarily affects unspayed female dogs. It can be life-threatening if left untreated. Spaying eliminates the risk of pyometra completely.
Ovarian cysts:
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries. They can cause pain and discomfort for female dogs. Spaying removes the ovaries, eliminating the possibility of ovarian cysts.
By spaying your female dog, you can significantly reduce her chances of developing these diseases and provide her with a healthier and longer life.
In conclusion, spaying is a surgical procedure that removes a female dog's reproductive organs. It helps prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduces the risk of certain health problems. Spaying is an important decision to consider for the well-being of your furry friend.
How long does it take a dog to recover from being spayed?
After undergoing spaying surgery, most pets will begin to feel improvement within 24-48 hours, but it typically takes about 10 to 14 days for them to fully recover. It is important during this timeframe to keep your pet relaxed and prevent them from jumping, as doing so could potentially reopen the incision.
Do female dogs change after being spayed?
After the surgical procedure of spaying or neutering, one of the most obvious changes in both male and female dogs is a reduction in aggression. This is because spaying and neutering lower the levels of hormones that can contribute to aggressive behavior, specifically testosterone in male dogs and estrogen in female dogs.
What do they do when they spay a dog?
Spaying is the medical term for the surgical procedure called ovariohysterectomy, which involves the complete removal of a female dog's ovaries and uterus to prevent reproduction. Some veterinarians now offer ovariectomy, where only the ovaries are removed.
What age should a female dog be spayed?
Neutering or spaying a toy or small breed puppy may be suitable between the ages of six to nine months, while for larger or giant breeds, it is recommended to wait until they are around 12 to 18 months old.
Should I stay home with my dog after being spayed?
It is advised to closely monitor them for the first 12 hours after their surgery. It is not required to stay awake or sleep beside your pet, and you can leave them alone for short periods of time as long as they are not at risk of licking their stitches.
How do I comfort my dog after being spayed?
When interacting with your dog, it is important to use gentle movements and avoid sudden motions. This will help calm their emotions and create a sense of peace. Additionally, as long as you provide enough food and water for them, you should not encounter significant difficulties during their recovery after spaying.